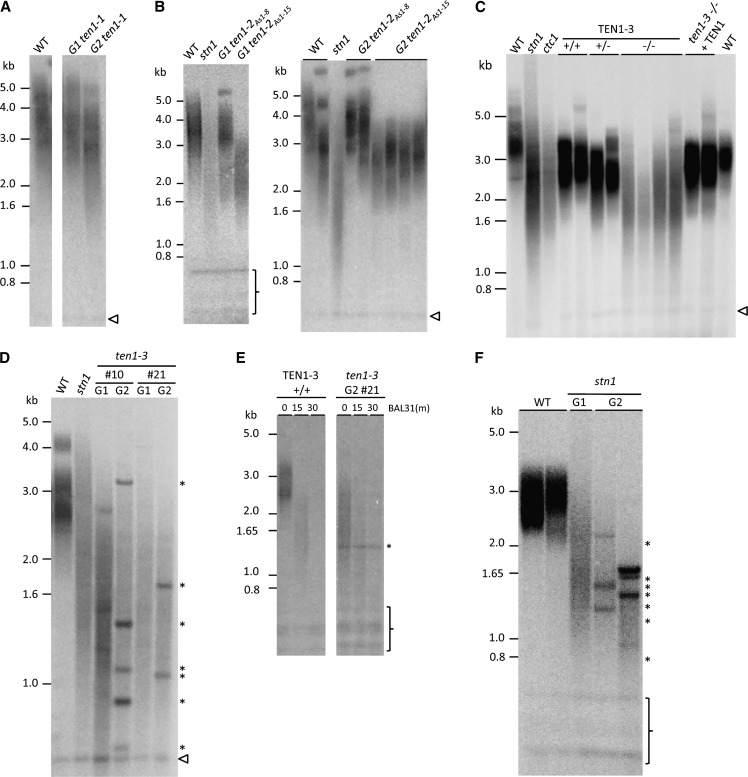
Figure 4.
TEN1 Is Important for Telomere Length Regulation and Genome Maintenance.
TRF analysis of ten1 mutants. Blots were hybridized with a radiolabeled G-rich telomeric probe.
(A) Results for first (G1) and second (G2) generation ten1-1 are shown relative to the wild type (WT).
(B) Telomere length in first (left) and second (right) generations of two antisense knockdown lines of TEN1. For comparison, results are shown with first generation stn1-1 mutants.
(C) TRF analysis of ten1-3 mutants. Results for offspring of ten1-3 heterozygous plants are analyzed.
(D) Parent-progeny analysis for two different ten1-3 mutants.
(E) BAL31 time course of DNA with the wild type and a G2 ten1-3 mutant.
(F) Telomere profile of G1 and G2 stn1-1 mutants. Asterisks indicated abnormally sharp TRF bands. Interstitial telomeric DNA repeats are denoted by the bracket or an arrowhead.