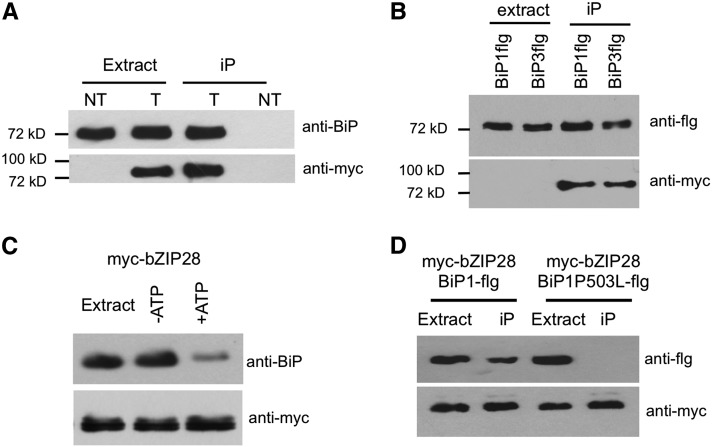
Figure 1.
BiP Binds to bZIP28.
(A) myc-bZIP28 was detected in extracts and immunoprecipitates (iP) from of roots of unstressed 7-d-old transgenic (T) and nontransgenic control (NT) Arabidopsis seedlings. Immunoblots were probed with anti-BiP and anti-myc antibodies. The anti-BiP antibody that was used for immunoprecipitations did not bind to agarose beads alone.
(B) Both BiP1-flg and BiP3-flg bind to myc-bZIP28. myc-bZIP28 was immunoprecipitated from extracts of N. benthamiana leaves transiently expressing BiP1-flg and BiP3-flg. Immunoblots were probed with anti-flg and anti-myc antibodies.
(C) BiP bound to myc-bZIP28 extracted from myc-bZIP28 expression lines is released by ATP. myc-bZIP28 was immunoprecipitated with anti-myc antibodies and incubated for 30 min with or without 2 mM ATP and 2 mM MgCl2. Immunoblot was probed with anti-BiP and anti-myc antibodies.
(D) Mutant BiP with a defect in substrate binding does not bind bZIP28. myc-bZIP28 coexpressed with BiP1-flg or BiP1P503L-flg in the transient expression system was immunoprecipitated with anti-myc antibodies. Immunoblot was probed with anti-flg and anti-myc antibodies.