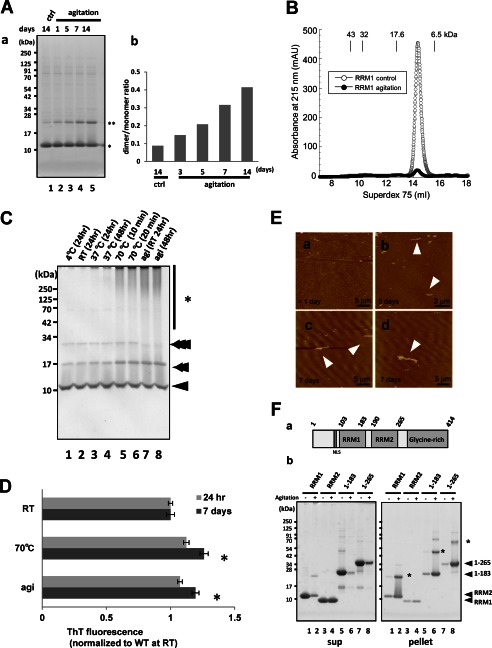
FIGURE 2.
Native RRM1 is a soluble monomer that is prone to aggregation. A, seeding effect of RRM1 aggregates assessed with disulfide-mediated dimers. The RRM1 proteins were agitated for 16 h or non-treated (ctrl), followed by postincubation at 4 °C for 1, 5, 7, or 14 days, and total protein mixture was separated by non-reducing SDS-PAGE. a, Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining; b, a densitometry for the ratio of the dimer to the monomer. B, gel filtration analysis showing the absorbance at 215 nm of RRM1 with (closed circles) or without (open circles) agitation. Agitation markedly reduces the amount of monomeric RRM1 in solution with no emergence of oligomers. Molecular size markers are ovalbumin (43 kDa), copper zinc superoxide dismutase (32 kDa), myoglobin (17.6 kDa), and aprotinin (6.5 kDa). C, Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining of a PFO-polyacrylamide gel (see “Experimental Procedures”) for the RRM1 domain after transient agitation or the application of heat stress. Single, double, and triple arrowheads indicate the monomer, dimer, and trimer sizes of RRM1, respectively. Asterisks indicate the high molecular weight species of RRM1. D, thioflavin T (ThT) fluorescence assay showing time-dependent amyloid formation of agitated RRM1. Recombinant WT RRM1 was incubated with BTA-1 at either 24 h or 7 days after 16-h agitation or static incubation at room temperature (RT) as a control. *, p < 0.05 versus control sample by one-way ANOVA of Bonferroni's test. Each value is expressed as ThT ratio to room temperature treatment with a 24-h postincubation (n = 3; ±S.E. (error bars)). E, atomic force microscope analysis of RRM1 aggregation after a 16-h agitation. Images show proteins on days 0 (a), 5 (b), and 7 (c and d). Large globular particles and fibrillar aggregates, indicated by arrowheads were present after agitation. F, a, schematic illustration of human TDP-43 with domain information. b, non-reducing SDS-PAGE analysis of RRM1, RRM2, and N-terminal fragments spanning RRM1 (aa 1–183) and RRM2 (aa 1–265), with or without overnight agitation. Protein solutions were separated into supernatant and pellet fractions after a 7-day incubation at 4 °C after the agitation. *, dimer forms of each protein (RRM1, aa 1–183 fragment, and aa 1–265 fragment).