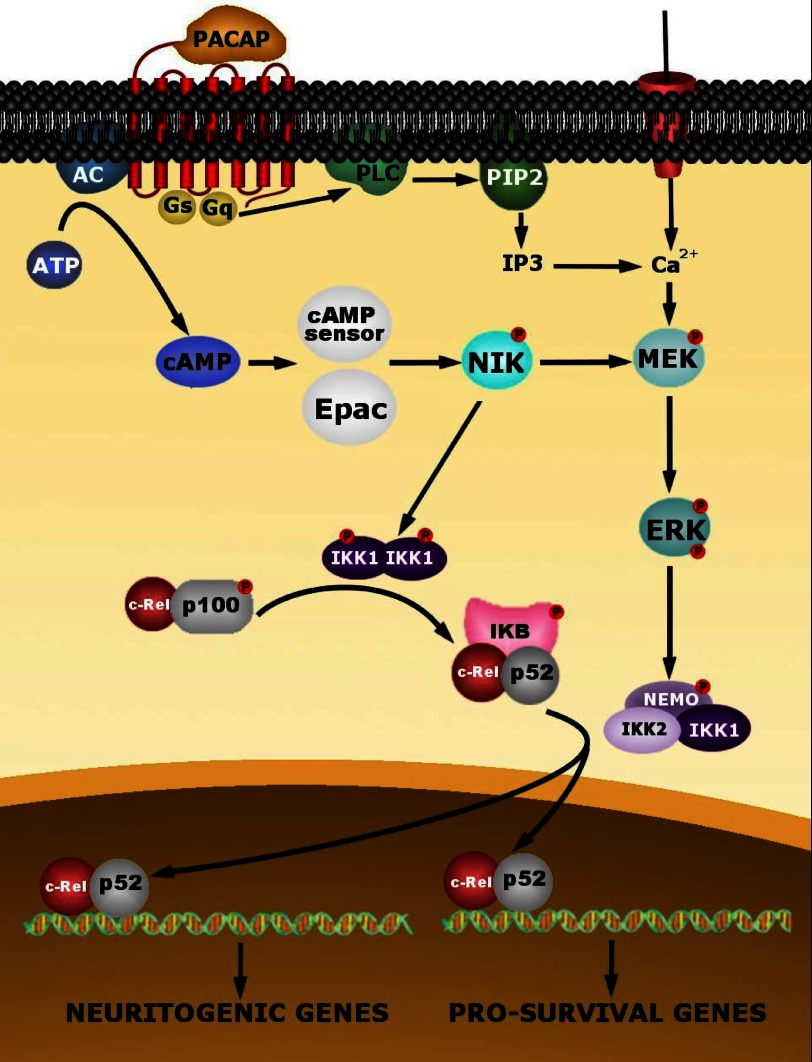
FIGURE 13.
Schematic representation summarizing the putative intracellular events involved in PACAP-induced NF-κB activation in PC12 cells. The effect of PACAP triggers a cAMP-dependent activation of NIK, probably through Epac or the new cAMP sensor (26). NIK, in turn, would activate IKK1 subunit of the IKK complex composed of a homodimer of the catalytic IKK1 permitting the production of c-Rel/p52 dimers which are maintained in the cytoplasm by the IκB protein. NIK also activates IKK2, a subunit of the heterodimeric IKK complex comprising the catalytic IKK1 and IKK2 subunits and the regulatory protein NEMO, through activation of the ERK1/2 kinases. The MAP kinase pathway could also be activated by Ca2+ mobilization. Activated IKK2 induces the release of c-Rel/p52 from IκB and its nuclear translocation to regulate the expression of genes implicated in PACAP-induced survival and neuritogenesis.