FIGURE 2.
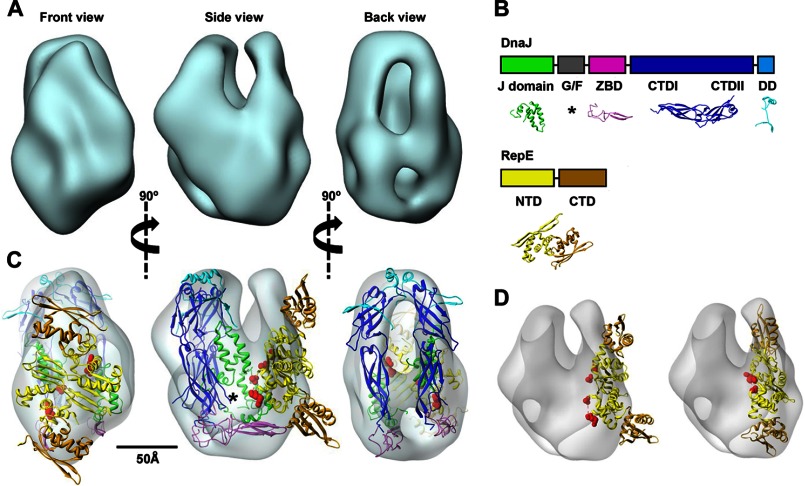
Architecture of the DnaJ-RepE complex. A, three-dimensional reconstruction of the DnaJ-RepE complex shown in three different, orthogonal views. B, domain arrangement of DnaJ and RepE proteins and structures used in this study: J-domain (green; PDB code 1XBL), ZBD (magenta; PDB code 1EXK), CTDI and CTDII domains (blue; PDB code 1NLT), and dimerization domain (DD) (cyan; PDB code 1XAO). Disordered G/F-domain is marked by an asterisk. In the RepE monomer, NTD and CTD are shown in yellow and brown, respectively (extracted from PDB code 2Z9O). C, docking of the atomic model of DnaJ and the atomic structure of RepE into the corresponding masses of the three-dimensional reconstruction; color coding is the same as in B. The disordered G/F-domain is tentatively located in the empty region marked by an asterisk. Red spheres indicate residues Ile46 and Asp57, located, respectively, at the beginning and end of Lα2-β2. See supplemental Movie S1 for an easier interpretation of the docking. D, docking of the DNA-bound RepE structure (PDB code 2Z9O) into the DnaJ-RepE complex three-dimensional reconstruction before (left) and after (right) applying flexibility to the monomers. A 25° tilt of the RepE C-terminal domains substantially improves the quality of the docking.