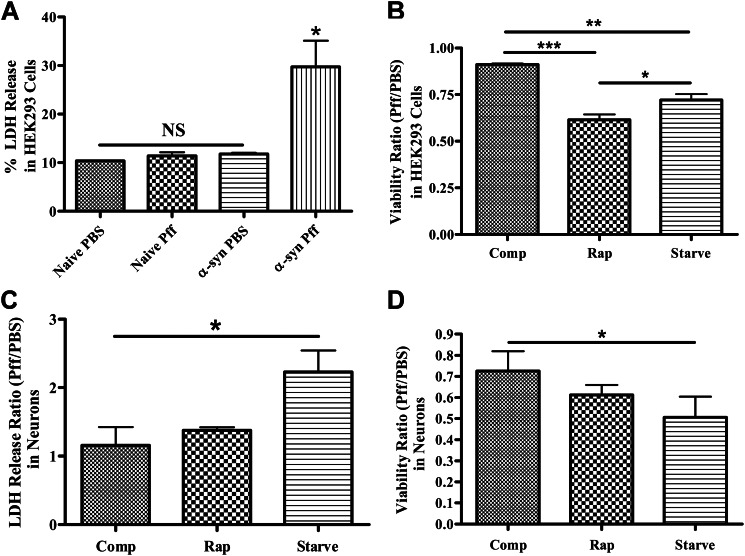
FIGURE 11.
Treatments that activate autophagy increase the toxicity of α-syn aggregates. A, lactate dehydrogenase release assay was performed to monitor cell death in naive HEK293 cells or HEK293 cells that express α-syn. Only Pff-tdHEK293 α-syn cells (α-syn Pff) showed significantly increased LDH release (n = 2). B, PBS- or Pff-tdHEK293 α-syn cells were maintained in nutrient-rich complete media (comp), treated with rapamycin or maintained in starvation media after transduction, until a tetrazolium-based viability assay was carried out. Both starvation and rapamycin treatment significantly reduced viability in transduced cells (n = 3). C and D, Pff- or PBS-td WT neurons were starved or treated with rapamycin, and the LDH release assay (n = 3) (C) and the viability assay (n = 2) (D) were performed. Starvation significantly increased cell death and decreased viability in neurons, and rapamycin treatment trended toward the same pattern. (Error bars, ±S.E. A and B, one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc analysis used to test for statistically significant differences. C and D, Student's paired t test was used to test for statistically significant differences. NS, *, ** and *** indicate p > 0.05, p < 0.05, p < 0.01, and p < 0.001, respectively.)