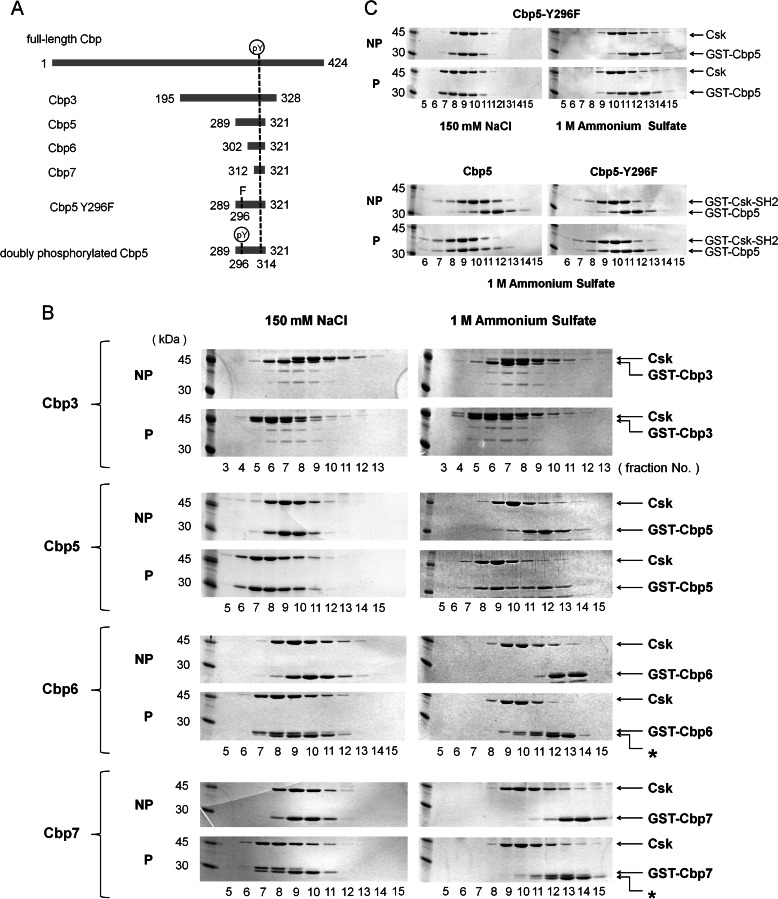
FIGURE 1.
Gel filtration assay using Cbp peptides of different lengths. A, schematic representation of intact Cbp and its various peptide fragments that appear in the text. The N- and C-terminal residue numbers are indicated on the left and right of each peptide. Tyr(P) represents the 296th or 314th phosphorylated Tyr. B, SDS-PAGE of gel-filtered fractions, including GST-fused Cbp3, Cbp5, Cbp6, or Cbp7, and Csk showing a secondary binding region between Lys-289 (N-terminal of Cbp5) and Ser-302 (N-terminal of Cbp6) on the N-terminal side of the Tyr(P) of Cbp. NP and P indicate the corresponding nonphosphorylated and phosphorylated Cbp peptides, respectively. Fractions simultaneously containing both the Cbp peptide and Csk indicate that the complex was formed in the corresponding condition. Asterisks indicate nonphosphorylated samples. C, SDS-PAGE of gel-filtered fractions, including GST-fused Cbp5-Y296F and Csk or GST-fused Csk-SH2, shows that Tyr-296 of Cbp is at least involved in the interaction with Csk or Csk-SH2. NP and P indicate the corresponding nonphosphorylated and phosphorylated Cbp peptides, respectively. All the gel filtration assays were performed in a buffer containing 150 mm NaCl (left) or 1 m (NH4)2SO4 (right).