Figure 1.
Sin1 is not required for T cell development.
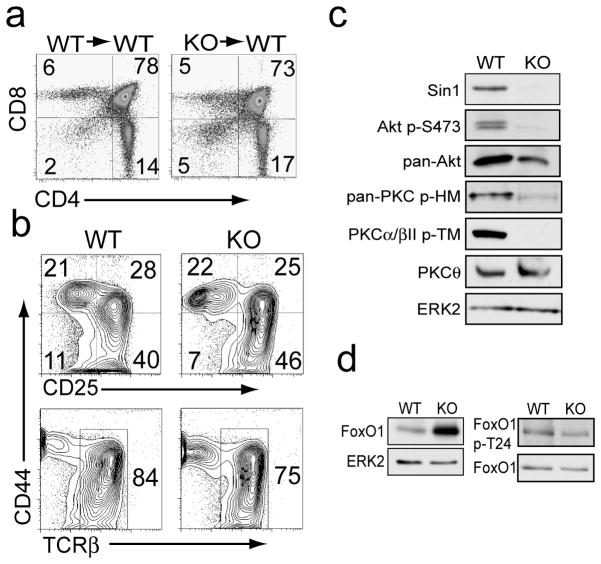
a) CD4+ and CD8+ cells in the thymus of Sin1+/+ (WT) or Sin1−/− (KO) chimeric mice were assessed by flow cytometry.
b) Sin1 WT or KO fetal liver cells were cultured on OP9-DL1 stromal cells with IL-7 to derive progenitor T cells. Cell surface expression of CD44, CD25 (upper panels) and TCRβ chain (lower panels) was measured by flow cytometry. Representative FACS plots of 1 WT and 2 independent Sin1 KO T cell cultures are shown.
c) Sin1 WT and KO T cells were cultured on OP9-DL1 stromal cells with IL-7 and then analyzed by immunoblotting for the indicated proteins. ERK2 serves as a loading control. Pan-PKC p-HM antibody (PKCβII p-S660) detects phosphorylated hydrophobic motif (HM) of PKC.
d) Total FoxO1 expression in WT and Sin1 KO T cells cultured on OP9-DL1 stromal cells with IL-7 was measured by immunoblotting. ERK2 serves as a loading control. FoxO1 phosphorylation at T24 in WT and Sin1 KO T cellswas measured by immunoblotting and normalized to total FoxO1. The data in c and d are representative of 1 WT and 2 KO T cell cultures from two independent experiments.