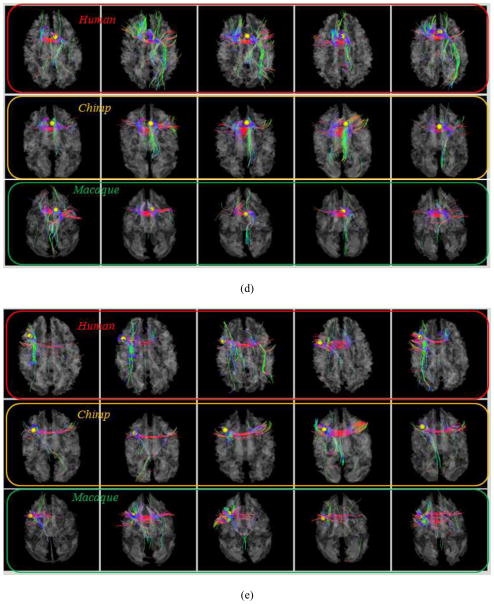
Fig. 8.
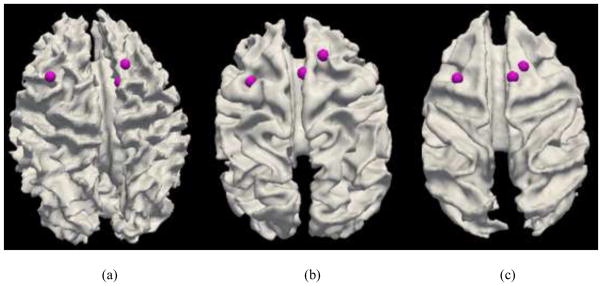
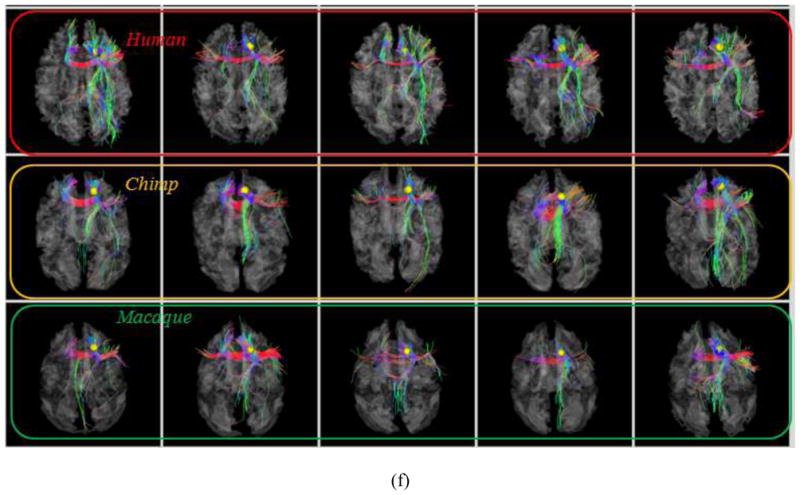
Examination of fiber connections of three functionally determined DICCCOLs. (a) Three activated functional brain regions (purple bubbles) in an auditory task-based fMRI in human brains. Other activated functional regions in human brains cannot find equivalents in chimpanzee and macaque monkey brains, and thus are not shown here. (b)–(c): The predicted regions in chimpanzee and macaque brains. (d) Visualization of fiber bundles of the first landmark in five human (top row), five chimpanzee (second row) and five macaque (bottom row) subjects. (e) Visualization of fiber bundles of the second landmark in five human (top row), five chimpanzee (second row) and five macaque (bottom row) subjects. (f) Visualization of fiber bundles of the third landmark in five human (top row), five chimpanzee (second row) and five macaque (bottom row) subjects.