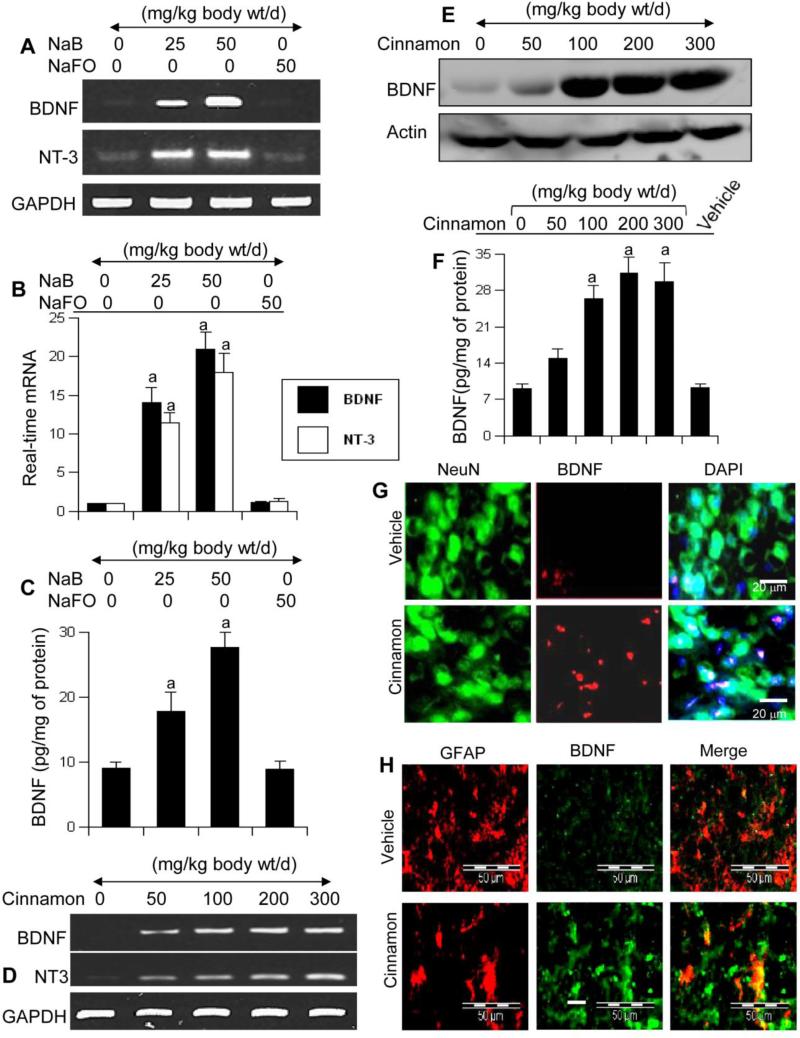
Figure 5. Oral administration of NaB and cinnamon increases the level of neurotrophic factors in vivo in the CNS of mice.
Six to eight week old male C57/BL6 mice (n=5 in each group) received different amounts of NaB via gavage and after 10 d of feeding, the mRNA expression of BDNF and NT-3 was monitored in the cortex by semi-quantitative RT-PCR (A) and real-time PCR (B). The protein level of BDNF in the cortex was quantified by ELISA (C). Similarly, mice (n=5 in each group) received different amounts of cinnamon powder (Cinnamonum verum) via gavage and after 10 d of feeding, the mRNA expression of BDNF and NT-3 was monitored in the cortex by semi-quantitative RT-PCR (D). Control mice received only vehicle (0.5% methylcellulose). The protein level of BDNF in the cortex was monitored by Western blot (E) and ELISA (F). Data are means ± SEM of five mice per group. sp < 0.001 vs control. Cortical sections were also double-labeled for NeuN & BDNF (G) and GFAP & BDNF (H). Results represent analysis of two sections of each of five mice per group.