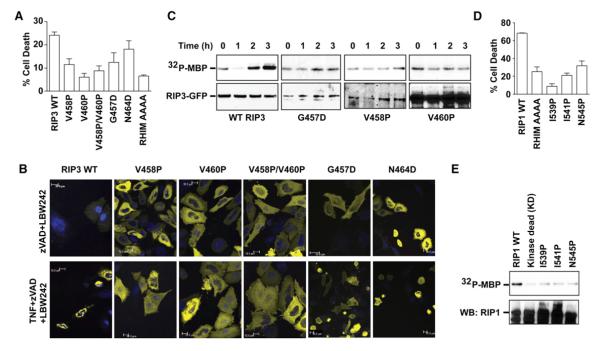
Figure 7. The RIP1/RIP3 Interaction Is Crucial for Kinase Activation, Clustering, and Cell Death.
(A) Effects of RIP3 mutations on TNF-induced necrosis in HeLa cells transfected with WTor the indicated RIP3 mutants fused to YFP. AAAA, quadruple Ala mutant of RIP3 at the VQVG RHIM sequence. Results shown are averages of triplicates ±SEM.
(B) Effects of RIP3 mutations on puncta formation in HeLa cells transfected with the indicated RIP3-YFP plasmids as examined by confocal microscopy.
(C) Effects of RIP3 mutations on kinase activity of the anti-RIP3 immunoprecipitates in RIP3−/− fibroblasts stably expressing the indicated RIP3-GFP mutants using MBP as the substrate. Bottom panel shows the RIP3 western blot of the same membrane.
(D) Effects of RIP1 mutations on TNF-induced necrosis in RIP1−/− fibroblasts transfected with the indicated RIP1 fused to GFP. Results shown are averages of triplicates ±SEM.
(E) Effects of RIP1 mutations on kinase activity of the anti-GFP immunoprecipitates in 293T cells transfected with the indicated RIP1-GFP constructs using MBP as the substrate. The same membrane was probed for RIP1 on western blot in the lower panel.
See also Figure S7.