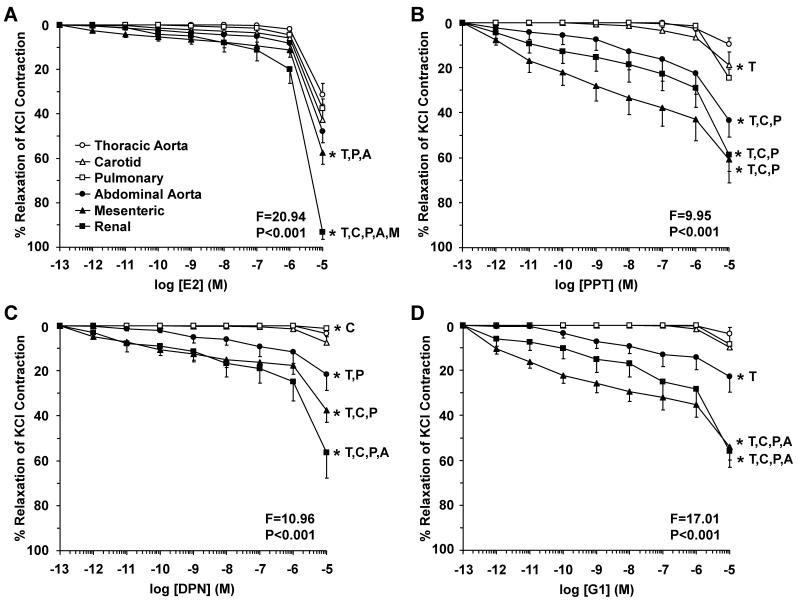
Fig. 12.
ER-mediated inhibition of Ca2+-dependent contraction in cephalic, thoracic and abdominal arteries of female rat. Endothelium-denuded segments of thoracic aorta (open circles), carotid (open triangles), pulmonary (open squares), abdominal aorta (closed circles), mesenteric (closed triangles) and renal artery (closed squares) were stimulated with high KCl (96 mM) depolarizing solution to induce a Ca2+-dependent contractile response in VSM. Increasing concentrations (10−12 to 10−5 M) of 17β-estradiol (E2, activator of most ERs) (A), PPT (ERα agonist) (B), DPN (ERβ agonist) (C), or G1 (GPR30 agonist) (D) were added and the % relaxation of KCl contraction was measured. Data represent means±SEM, n= 8 to 10. * Significantly different (p<0.05) from corresponding measurement in thoracic aorta [T], carotid [C], pulmonary [P], abdominal aorta [A], mesenteric [M] and renal artery [R].