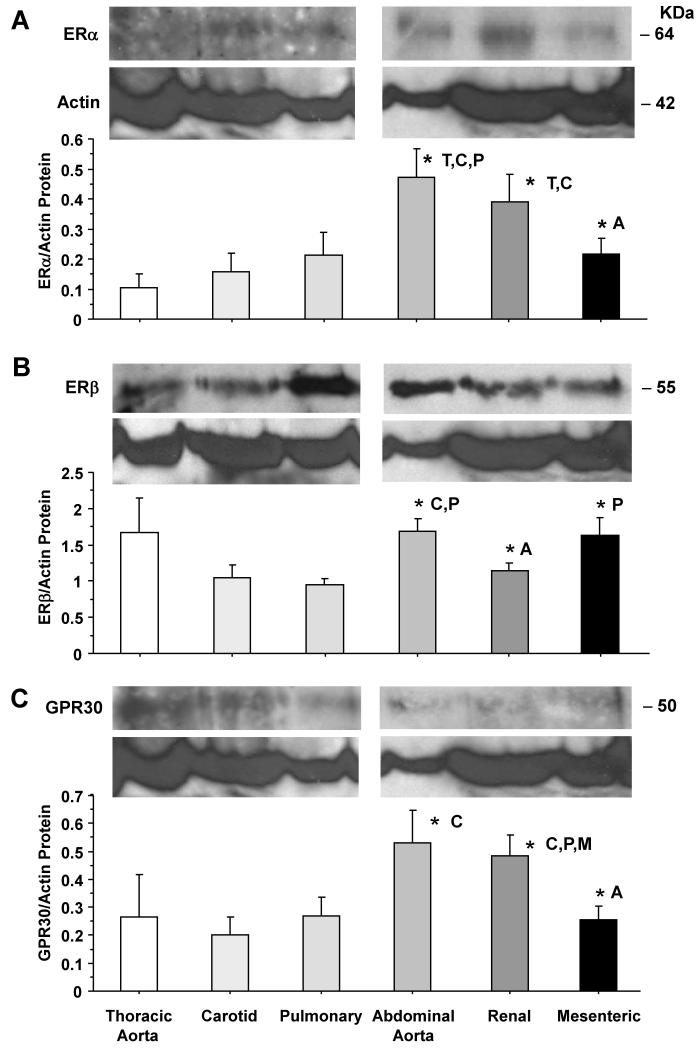
Fig. 5.
ERα, ERβ and GPR30 protein amount in cephalic, thoracic and abdominal arteries of female rat. Tissue homogenate of thoracic aorta, carotid, pulmonary, abdominal aorta, renal and mesenteric artery were prepared for Western blot analysis. ER subtypes were detected using antibodies to ERα (1:500) (A), ERβ (1:1000) (B) and GPR30 (1:500) (C). Blots for cephalic and thoracic arteries (aorta, carotid, pulmonary) as compared to abdominal arteries (abdominal aorta, renal, mesenteric) were performed on different gels. The representative immunoblots for the abdominal aorta, renal, and mesenteric artery in panels B and C have the same actin because the blots were first reacted with GPR30 antibody, stripped, then reacted with ERβ antibody, stripped, then reacted with actin antibody. The intensity of the immunoreactive bands was analyzed using optical densitometry, and normalized to the house keeping protein actin. Data represent means±SEM, n= 8 to 10. * Significantly different (p<0.05) from corresponding measurement in thoracic aorta [T], carotid [C], pulmonary [P], abdominal aorta [A], mesenteric [M] and renal artery [R].