Fig. 3.
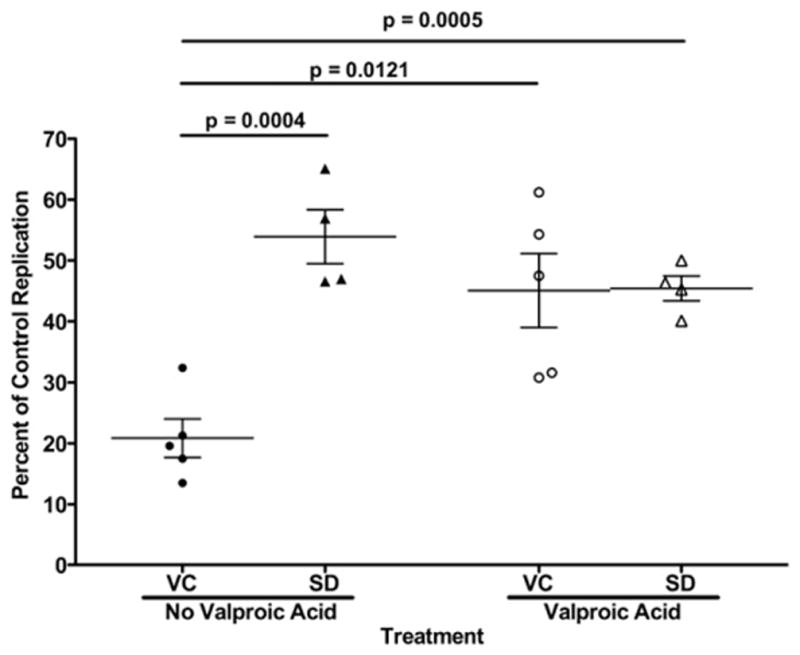
Valproic acid inhibits contact-mediated CD8+ T-lymphocyte noncytolytic suppression in virus controllers. HIV-1-infected primary CD4+ T-lymphocytes were cultured in direct contact with or without autologous CD8+ T-lymphocytes at a 2:1 effector to target ratio. CD8+ T-lymphocytes from virus controllers (VC, circles) or seronegative donors (SD, triangles) were examined. Noncytolytic suppression was examined in the absence and presence of valproic acid (filled and open symbols, respectively). Virus controller CD8 T cell co-cultures without valproic acid had significantly lower HIV-1 replication than seronegative CD8+ T cell co-cultures without and with valproic acid (unpaired t-test, p=0.0004 and p=0.0005). HIV-1 replication in the virus controller CD8+ T-lymphocyte co-cultures significantly increased with the addition of valproic acid (paired t-test, p=0.0121). There was not a significant increase in replication in the seronegative CD8+ T-lymphocyte co-cultures (paired t-test, p=0.2187). Means and standard error are represented by horizontal and vertical lines respectively.
