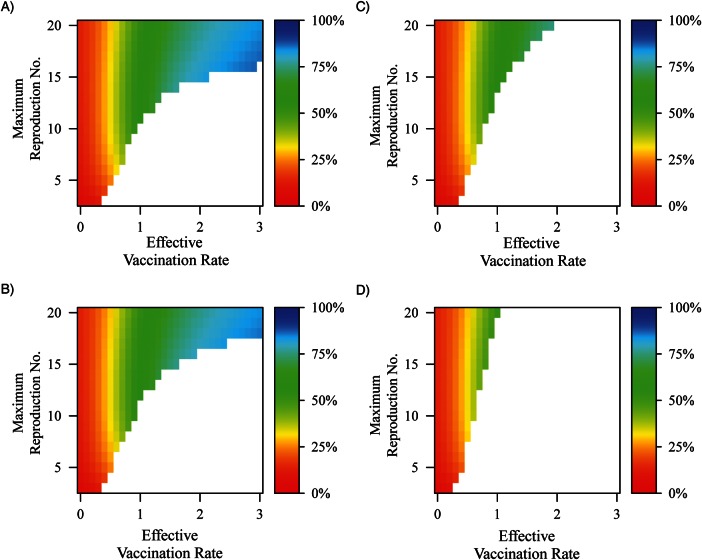
Figure 5.
Depiction of the proportion of the force of infection that is due to reinfections across vaccination rate and R0, where oral polio vaccine (OPV) transmissibility relative to wild poliovirus (WPV) transmissibility is set to A) 2.5%, B) 5%, C) 10%, and D) 20%. Reinfection is defined as WPV infection that occurs after an initial infection caused by an earlier WPV infection, vaccination, or infection due to OPV transmission. Waning rates are set such that it takes 10 years to increase susceptibility by 50%, contagiousness of any resulting infection by 16%, and duration of any resulting infection by 16%. In the white areas of the graph, there is not sustained transmission to calculate the force of infection (i.e., prevalence equals zero).