Fig. 1.
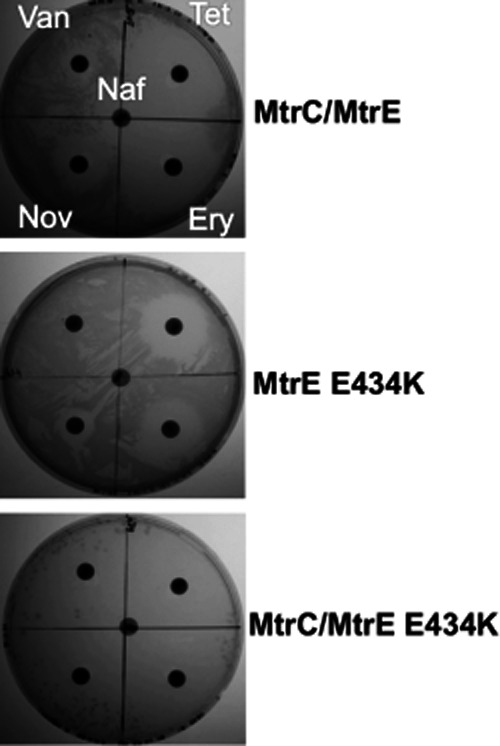
An E434K derivative of MtrE can be used to detect channel opening. Disc-diffusion assays were used to determine if KAM3(DE3) E. coli cells expressing mtrCDE genes and mutants were susceptible to vancomycin, which can be used as a marker of whether the OMP MtrE is open or closed, since it is too large to readily diffuse across the OM but can enter cells via an open OMP. A set of plates showing the disc-diffusion assays for cells expressing (i) MtrC and MtrE, (ii) MtrE E434K and (iii) MtrC and MtrE E434K. It is notable that cells expressing MtrE E434K alone were insensitive to vancomycin, MtrC/MtrE were moderately sensitive to vancomycin, and MtrC/MtrE E434K failed to grow in the presence of vancomycin. Disc-diffusion assays were performed in triplicate, generally assaying for growth around discs impregnated with the following antibiotics: vancomycin (Van; 30 μg), nafcillin (Naf; 1 μg), tetracycline (Tet; 30 μg), erythromycin (Ery; 10 μg) and novobiocin (Nov; 5 μg).
