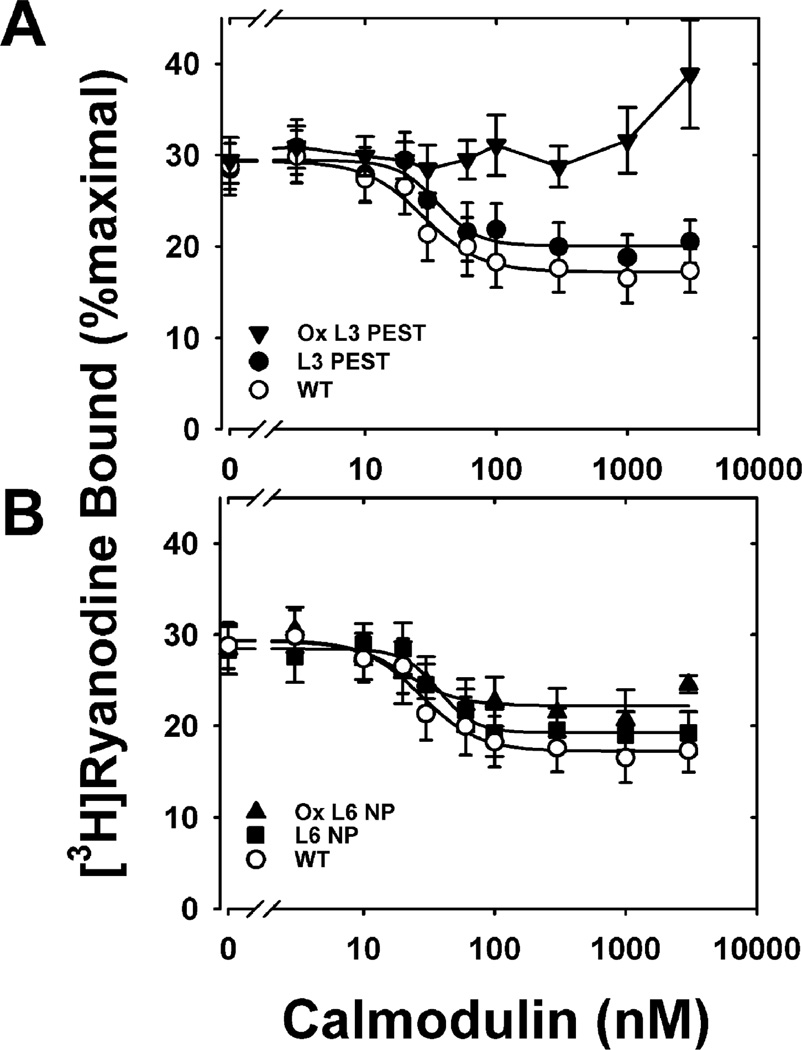
Figure 6.
Inhibition of skeletal muscle RyR1 [3H]ryanodine binding for WT and mutant L3PEST and L6NP CaM: (A) nonoxidized WT (○), nonoxidized L3PEST (●), and oxidized L3PEST (▼); (B) nonoxidized WT (○), nonoxidized L6 NP (■), and oxidized L6 NP (▲). RyR1 ryanodine binding was performed as described under Experimental Procedures in medium containing 700 µM Ca2+. Solid lines represent fits to a four-parameter Hill equation. Data are the mean ± SEM of six to ten experiments performed in duplicate. Table 2 reports the kinetic parameters derived from these fits, i.e., extent of inhibition of ryanodine binding, the concentration of CaM required to achieve half-inhibition of ryanodine binding (IC50), or the Hill coefficient (ni) of ryanodine binding for each fit.