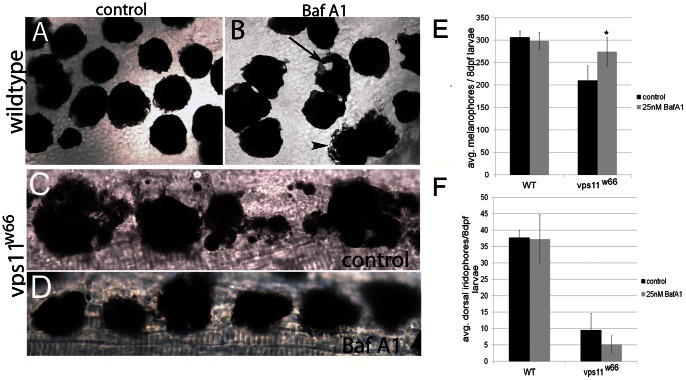
Figure 5. Treatment with bafilomycin A1 restores melanophore morphology and survival in vps11w66 mutants.
A) Dorsal head image (63X) of fixed, 8dpf wildtype larvae. Cells appear completely rounded, as expected following epinephrine induced melanosome aggregation. No vacuoles are observed. B) Dorsal head image of wildtype larvae treated with 25 nM bafilomycin A1 (Baf A1). Cell shape is less rounded, indicating reduced or incomplete melanosome aggregation (arrowhead). Large vacuoles are apparent (arrow). C, D) Dorsal anterior trunk images (63X) of vps11w66 mutant melanophores treated with control (1% DMSO) or 25 nM Baf A1 in embryo media. Cell fragmentation and irregular cell morphology is partially rescued with Baf A1 treatment. E, F) Quantification of melanophores (dorsal and lateral stripes; E) or iridophores (F) in 8dpf wildtype and vps11w66 mutant larvae treated with control (1% DMSO) or 25 nM Baf A1 embryo media. Only melanophores show significant increase in number following Baf A1 treatment. Two way ANOVA indicates a significant interaction between Baf A1 treatment and genotype. One way ANOVA and Bonferonni multiple comparisons analysis examining melanophore numbers within AB and vps11w66 groups, indicates a significant increase in Baf A1 treated vps11w66 larvae as compared to untreated controls (p<0.01*). Error bars are standard deviation.