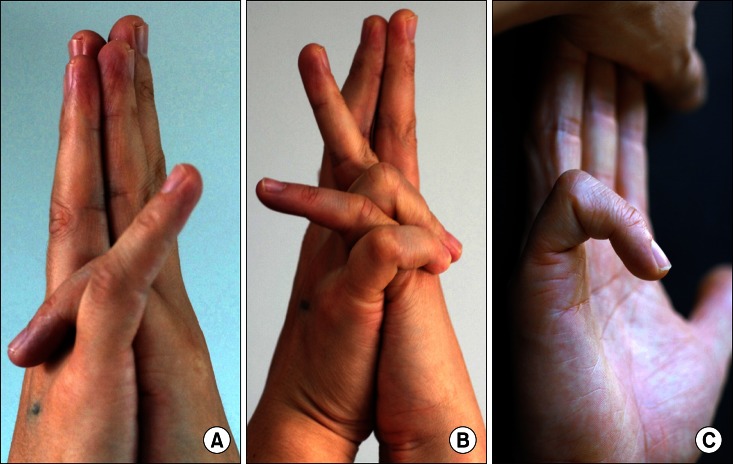
Fig. 3.
The flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS) connection between the little and ring fingers of the right hand. (A) Inability of flexing the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint of the little finger of the right hand to touch the target by our new test, in contrast to the little finger of the left hand. (B) When the adjacent ring finger was permitted to flex together, the little finger could flex the PIP joint to reach the aim. Full flexion of the adjacent ring finger was recorded as the close connection between the little and ring fingers. (C) However, this case exhibited independent FDS function of the little finger when tested by the expanded method.