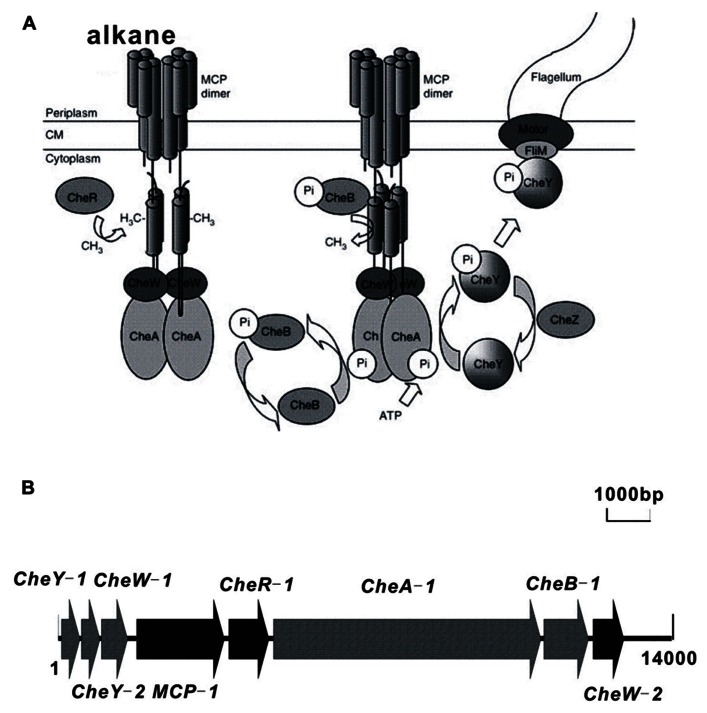
FIGURE 1.
Schematic diagram of the chemosensory signaling system of A. dieselolei B-5. (A) MCP dimers with associated CheW and CheA proteins are shown in the presence (left) and absence of alkane (right). Cells responding to a gradient of attractant will sense the attractant bound to the periplasmic side of the cognate MCP and will continue swimming in the favorable direction due to the inability of CheA to autophosphorylate. In the absence of CheA-P, CheY remains in the inactive unphosphorylated state, and swimming behavior remains unchanged. Cells swimming down a gradient of attractant will sense the decrease in attractant concentration due to decreased occupancy of the MCPs. Under these conditions, the MCPs undergo a conformational change that is transmitted across the cytoplasmic membrane and stimulates CheA kinase activity. CheA-P phosphorylates CheY, which in its phosphorylated state binds to the FliM protein in the flagellar motor and causes a change in the direction of flagellar rotation allowing the cell to randomly reorient and swim off in a new direction. Dephosphorylation of CheY-P is accelerated by the CheZ phosphatase. Under all conditions, the constitutive methyltransferase CheR methylates specific glutamyl residues on the cytoplasmic side of the MCP. Methylated MCPs stimulate CheA autophosphorylation, thus resetting the system such that further increases in attractant concentration can be detected. The methylesterase, CheB, becomes active when it is phosphorylated by CheA-P. CheB-P competes with CheR and removes methyl groups from the MCPs. CM, cytoplasmic membrane. (B) Organization of chemotaxis genes involved in alkane metabolism in A. dieselolei B-5. The detailed information of the ORFs of MCP gene cluster is presented. MCP, methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein; CheY-1, CheY-like receiver protein; CheY-2, CheY-like receiver protein; CheW-1, CheW-like protein, signal transduction protein; CheW-2, Chemotaxis protein, signal transduction protein; CheA, CheA signal transduction histidine kinase; CheB, CheB methylesterase; CheR, CheR methyltransferase.