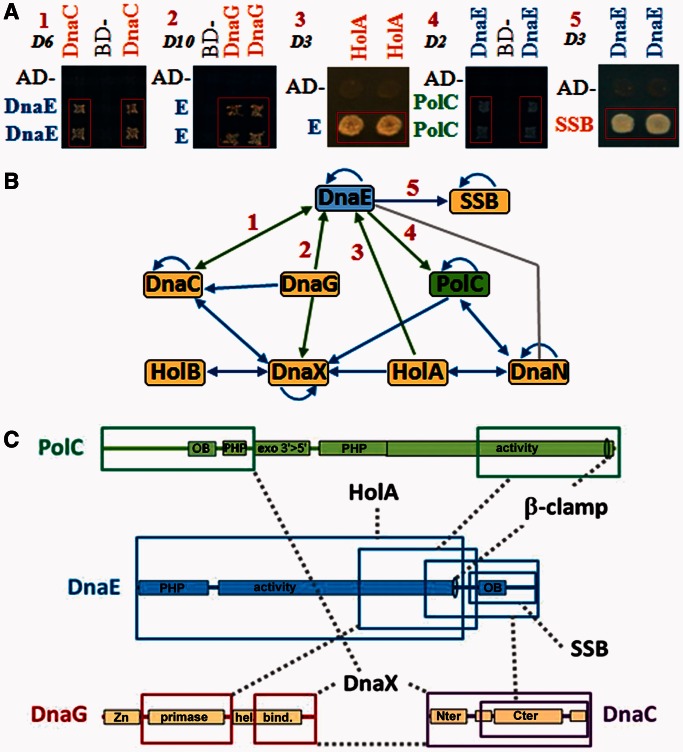
Figure 1.
DnaEBs interacts with the replicative helicase DnaC and primase DnaG. (A) Yeast two-hybrid matrix interaction assays illustrating interactions of DnaEBs with DnaC, DnaG, PolC, HolA and SSB. The indicated proteins were expressed as baits (Gal4 Binding Domain fusion) and/or as preys (Gal4 Activating Domain fusion). Pairs of independent diploid yeast cells expressing combinations of fusions were subjected to selection for the Adenosine+ phenotype as described in ‘Materials and Methods’ section and Supplementary Data. The empty bait and prey vectors (BD and AD) were used as negative controls. Plates were incubated at 30°C for the time indicated at the top left of each panel (in days). 1: AD-DnaEBs805–1115 and BD-DnaC; 2: AD-DnaEBs and BD-DnaG; 3: AD-DnaEBs1–826 and BD-HolA; 4: AD-PolC875–1437 and BD-DnaEBs618–1115; 5: AD-SSB and BD-DnaEBs618–1115. (B) Overview of replisomal interactions. Arrows are oriented from the bait to the prey. Blue: known interactions; green: new interactions; grey: interaction showed previously biochemically (14,19). (C) Schematic representation of protein-binding domains. Coloured boxes: protein binding domains; dashed grey lines: identified interactions. PHP: polymerase and histidinol phosphatase domain; activity: polymerase domain; OB: OB-fold; Zn: zinc finger binding domain; primase: primases conserved region; hel. bind.: helicase binding domain; Nter and Cter: DnaB-like helicases N- and C-terminal conserved domains.