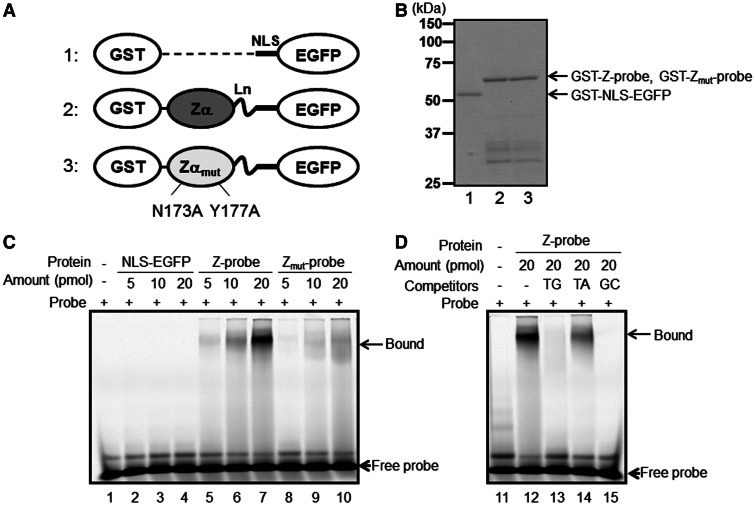
Figure 2.
The recombinant Z-probe binds to a Z-DNA-forming sequence in vitro. (A) A schematic figure of the recombinant proteins. 1: NLS-EGFP; 2: Z-probe; 3: Zmut-probe. The proteins were expressed as GST fusion proteins and purified using glutathione-conjugated beads. Zα: human ADAR1 Zα domain; Zαmut: the Zα domain possessing N173A and Y177A mutations corresponding to human ADAR1 residue numbers; Ln: (Gly4–Ser)3 linker residues. Detailed information is provided as Supplemental Figure S1. (B) SDS–PAGE analysis of the purified recombinant proteins. 1: GST-NLS-EGFP; 2: GST-Z-probe; 3: GST-Zmut-probe. A gel shift assay was performed using Cy5-labeled d(TG/AC)18 double-stranded oligonucleotides as probes. (C) The purified GST-NLS-EGFP vector (lanes 2–4), GST-Z-probe (lanes 5–7) and GST-Zmut-probe (lanes 8–10) were incubated with a Cy5-labeled oligonucleotide probe. Protein–DNA complexes were separated using native PAGE, and the fluorescence signals were detected using Typhoon FLA9000. (D) The GST-Z-probe (lanes 12–15) was incubated with excess non-labeled competitors (lanes 13–15) and mixed with a Cy5-labeled probe. Subsequently, the protein–DNA complexes were separated using native PAGE, and the fluorescence signals were detected. Competitors: TG: d(TG/AC)18 (lane 13); TA: d(TA/AT)18 (lane 14); GC: d(GC/CG)18 (lane 15).