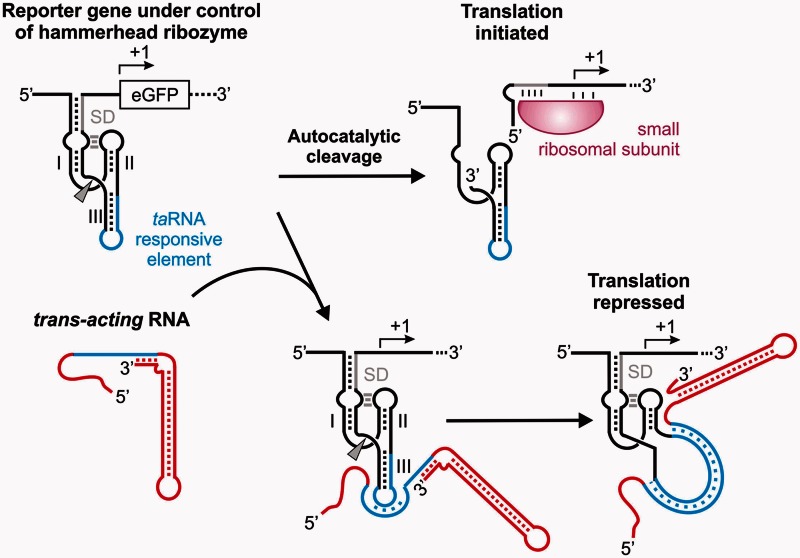
Figure 1.
Mechanism of trans-acting sRNA controlling a hammerhead ribozyme. Expression of an eGFP reporter gene is post-transcriptionally controlled by a TR-HHR. An extended stem 1 of the TR-HHR sequesters the ribosomal binding site. In addition, stem 3 harbors a TR element (blue), which in the absence of a taRNA folds into a catalytically active ribozyme conformation. Autocatalytic cleavage (marked by an arrowhead) frees the RBS resulting in binding of the small ribosomal subunit and initiation of translation. Upon expression of a trans-acting RNA (red), an RNA–RNA hybrid between the complementary sequences (blue) within the taRNA and the TR-HHR is formed. A single-stranded seed region of the taRNA hybridizes to the complementary nucleotides located in the loop region of stem 3. Full hybridization unzips stem 3 of the TR-HHR rendering the HHR catalytically inactive and repressing translation.