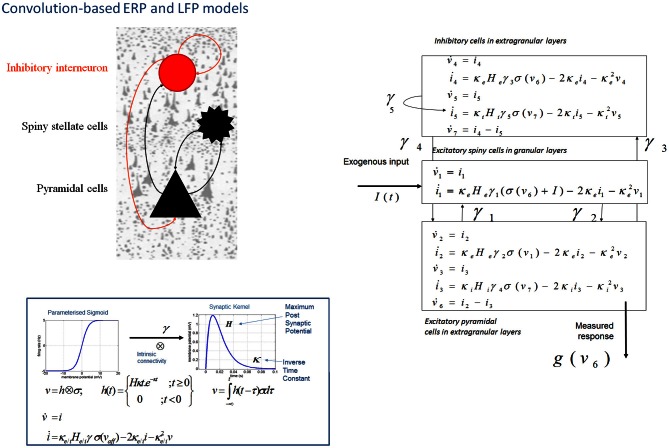
Figure 1.
Convolution-based neural mass models: “ERP” and “LFP”. Neural mass model used to represent a cortical source. Three cell subpopulations contribute to the ongoing dynamics. These include spiny stellate cells in granular layer IV, pyramidal cells and inhibitory interneurons in extra granular layers (II and III; V and VI). Intrinsic connections, γ1,2,3,4,5 link subpopulations in each source. Neuronal states include currents, i, and membrane potentials v. Extrinsic connections enter at specific cortical layers (see main text). Right: The functions controlling ongoing dynamics and their parameterization are summarized by synaptic kernels, which are used to convolve presynaptic (firing) input [a sigmoidal function of presynaptic membrane depolarization σ(v)] to produce postsynaptic depolarization (v), dependent on membrane time constants (1/κe/i) and average post-synaptic depolarizations (He/i) at excitatory (e) and inhibitory (i) synapses.