Figure 1. The role of oxidant stress in aging and age-related disease.
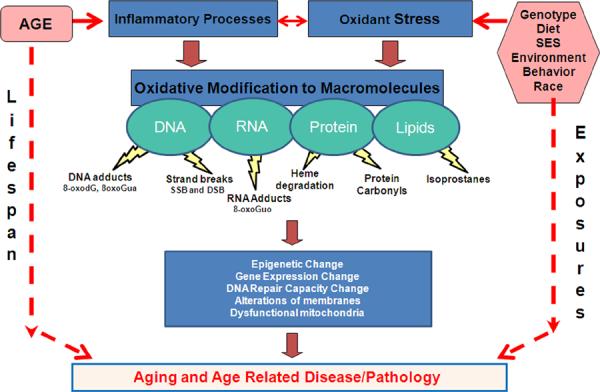
Both non-modifiable risk factors (age, race, genotype) and modifiable risk factors (diet, socioeconomic status, environment) have the propensity to interact with and affect the inflammatory processes and affect and be affected by oxidant stress. The interaction of all of these parameters can result in oxidative modifications of cellular macromolecules DNA, RNA, lipid and proteins. These oxidative modifications alone or in association with other biologic factors can lead to epigenetic changes, changes in both gene expression and DNA repair capacity, or mitochondrial and membrane dysfunction.
