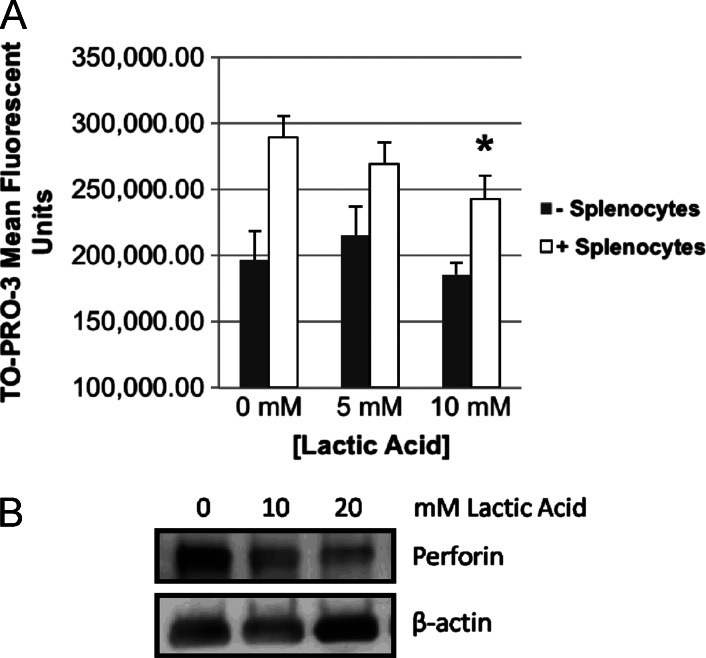
Figure 6.
Lactic acid inhibits CMI and decreases lymphocyte perforin levels specific to our HPV+ HNSCC tumor model. (A) CMI assay. CFSE-stained E6/E7/Ras cells were irradiated (30 Gy) and co-cultured for 24 hours with isolated mixed lymphocytes from the spleens of mice vaccinated with Ad5 E6/E7 [6] at 0, 5, and 10 mM lactic acid in media (RPMI) followed by dead cell staining (TO-PRO-3) and flow cytometry. CFSE-positive cells were gated and mean TO-PRO-3 signal averaged (n = 3) for each dosage group. In all dosage groups, the presence of lymphocytes led to significantly increased dead cell staining (P < .02), while lactic acid in the absence of lymphocytes did not itself induce any cell death (splenocytes: 0, 5, and 10 mM, NS). A trend of decreasing dead cell staining with increasing lactic acid concentration was observed. At 10 mM lactic acid, cell-mediated cytotoxicity was significantly decreased as indicated by decreased dead cell staining (*P < .005). (B) Lymphocytes cultured alone in lactic acid for 24 hours showed a dose-dependent decrease by Western blot in total perforin, the primer of CMI. Concentrations of lactic acid at 10 mM and higher were tested as significant inhibition of CMI was not seen at less than 10 mM. The blot has been cropped for presentation and canbe seen infull in Figure W2.