Abstract
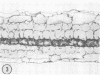
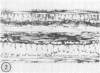
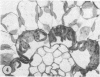
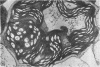
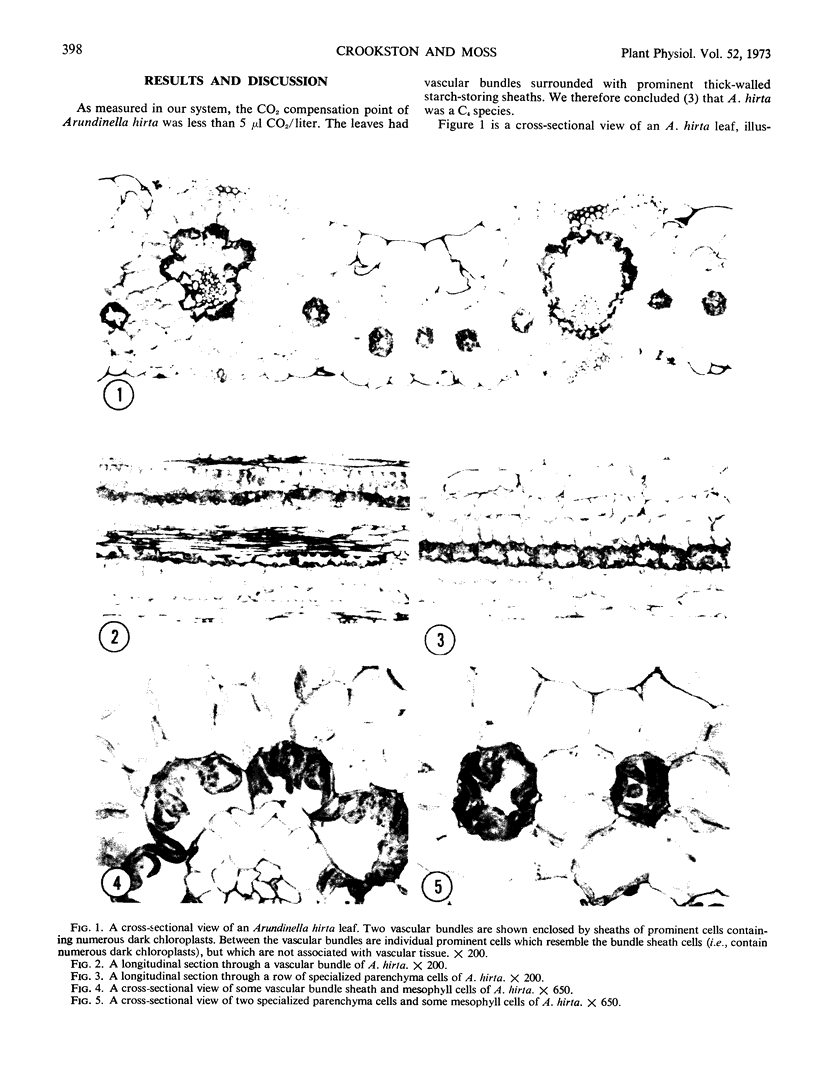
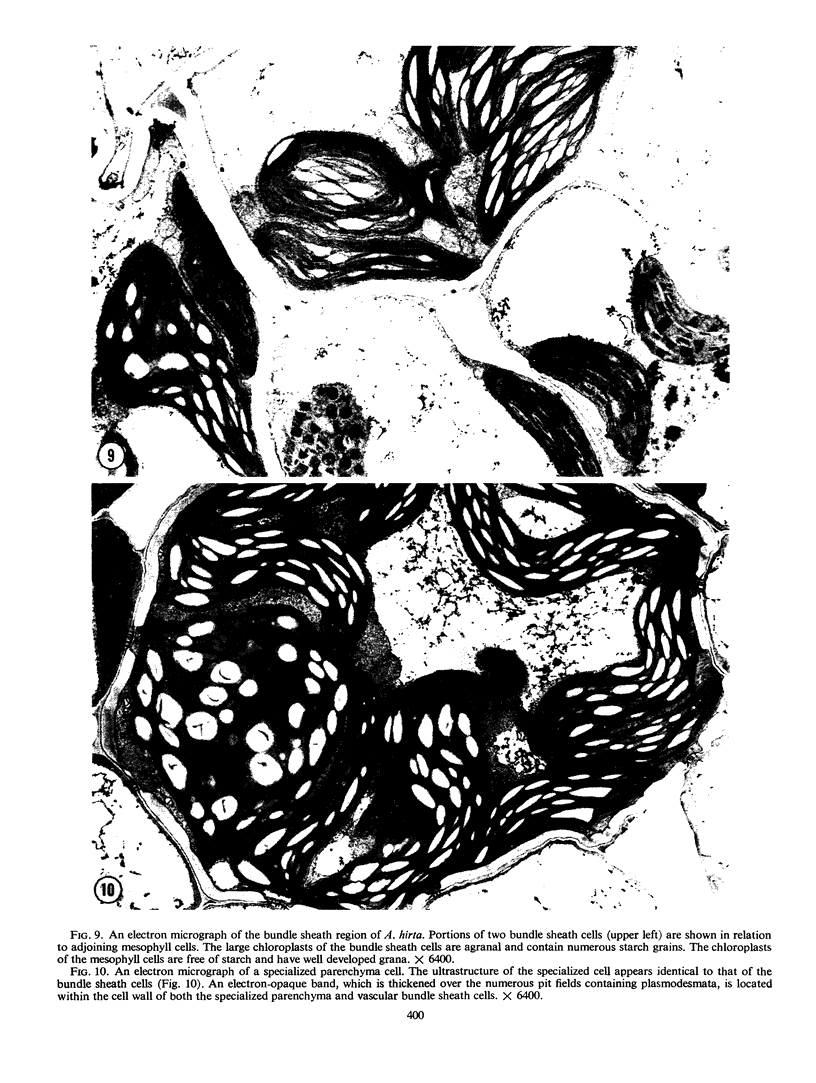
The species Arundinella hirta L. posseses a striking variation of the leaf anatomy that is characteristic of C4 grasses. In addition to a sheath of large, bright green cells around the vascular bundles, there are strands of large parenchyma cells which appear identical to the bundle sheath cells and which run parallel to the vascular bundles, but which are not associated with any vascular tissue. This species may be useful for studying the cellular compartmentalization associated with the C4 pathway and should provide interesting material for determining the role of translocation in the functioning of the C4 system.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crookston R. K., Moss D. N. The relation of carbon dioxide compensation and chlorenchymatous vascular bundle sheaths in leaves of dicots. Plant Physiol. 1970 Oct;46(4):564–567. doi: 10.1104/pp.46.4.564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch M. D. The C 4 -pathway of photosynthesis. Evidence for an intermediate pool of carbon dioxide and the identity of the donor C 4 -dicarboxylic acid. Biochem J. 1971 Nov;125(2):425–432. doi: 10.1042/bj1250425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss D. N., Willmer C. M., Crookston R. K. CO(2) Compensation Concentration in Maize (Zea mays L.) Genotypes. Plant Physiol. 1971 Jun;47(6):847–848. doi: 10.1104/pp.47.6.847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spurr A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Jan;26(1):31–43. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]