Figure 1. Typical anatomical and functional coronary images using magnetic resonance imaging at rest and with isometric handgrip stress.
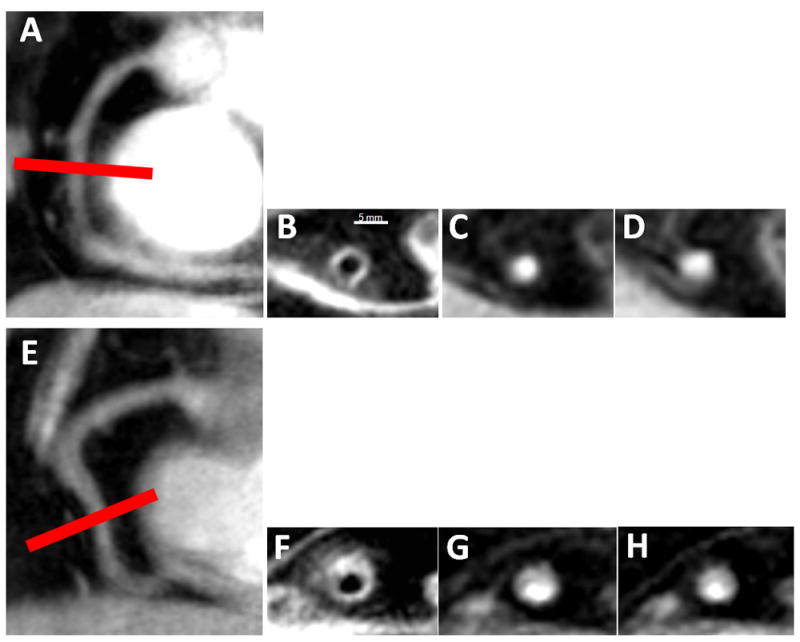
In a healthy subject, in image A, a scout scan obtained along the RCA (right coronary artery) in a healthy adult subject is shown together with the location for cross-sectional imaging (red line). In B, a view perpendicular to the RCA in a healthy adult subject is shown, illustrating a black blood vessel wall cross section. In C, a view perpendicular to the RCA in a healthy subject is shown at rest (C) and during stress (D). In a patient with CAD, shown in images E-H, a scout scan obtained parallel to the RCA is shown (E) together with the location for cross-sectional imaging (red line). F: RCA black blood vessel wall cross-sectional image in the same CAD patient. In G, a view perpendicular to the RCA in a CAD patient is shown at rest (G) and during stress (H).
