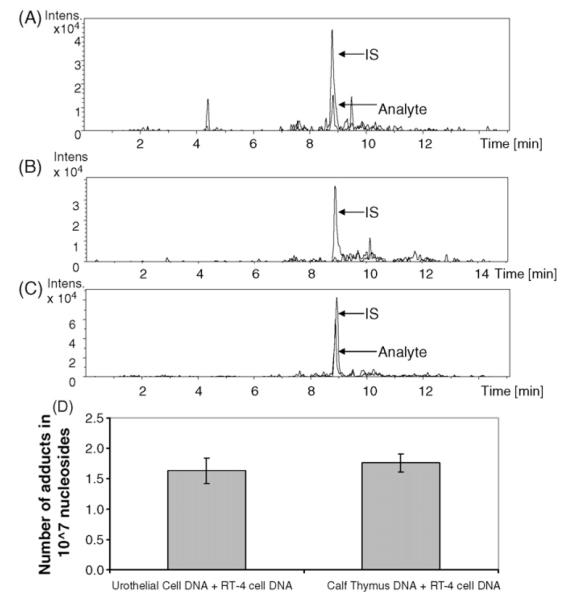
Fig. 8.
Analysis of dG-C8-4-ABP adducts by digesting 1 μg of DNA. (A) Chromatogram of dG-C8-4-ABP from the processing of 1 μg of DNA (equivalent of 250 ng injected on-column) in bladder sample of rat dosed with 25 mg/kg 4-ABP. Signal corresponds to 7±2 adducts in 107 nucleotides, which is the same as that obtained from the analysis of a 5 μg digest. (B) Representative chromatogram from the analysis of a 1 μg urothelial cell DNA digest of a lifetime non-smoker. The dG-C8-4-ABP adduct was not detected but the response of the internal standard has not been compromised by the urothelial cell matrix. (C) Analysis of dG-C8-4-ABP from two pooled urothelial cell samples; 1 μg DNA was digested and spiked with IS and 2.24 fmol dG-C8-4-ABP. On-column injection of 250 ng corresponds to injection of 14±3 adducts in 107 nucleosides. (D) Determination of digestion efficiency of urothelial cell DNA. Comparison of dG-C8-4-ABP adduct levels in 1 μg exfoliated urothelial cell DNA and 1 μg calf-thymus DNA, each spiked with 10 ng 4-ABP-modified DNA prior to digestion. No statistical differences are observed.