Table 1.
Ranking of affinities for chaperone PapD using relaxation-edited 1H-NMR spectroscopy (Relative PapD affinity) and evaluation of inhibitory activity of P pilus biogenesis in HB101/pPAP5 at a concentration of 1.8 mM compound (HA-titer).
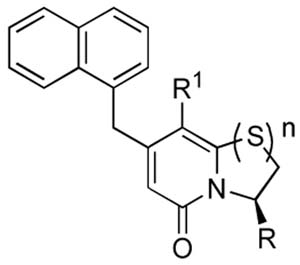
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Compound | R1 | R | n | Relative PapD affinity (%)a | HA-titerd |
| 1 | 1 | phenyl | -CO2Li | 1 | -b | -e |
| 2 | 2 | cyclopropyl | -CO2Li | 1 | 71 | 8 |
| 3 | 11 | phenyl | -CONHSO2Ph | 1 | -b | 4g |
| 4 | 12 | cyclopropyl | -CONHSO2Ph | 1 | 100 | 4 |
| 5 | 9 | phenyl | -CONHSO2Me | 1 | -b | 4 |
| 6 | 10 | cyclopropyl | -CONHSO2Me | 1 | 62c | 2 |
| 7 | 15 | phenyl | -tetrazole | 1 | -b | 2g |
| 8 | 16 | cyclopropyl | -tetrazole | 1 | 67 | 4 |
| 9 | 5 | phenyl | -CONHOH | 1 | -b | 128f |
| 10 | 6 | cyclopropyl | -CONHOH | 1 | 52 | 64f,g |
| 11 | 13 | phenyl | -CONH2 | 1 | -b | 64f |
| 12 | 14 | cyclopropyl | -CONH2 | 1 | 40 | 64 f |
| 13 | 19 | phenyl | -CO2Hh | 0 | -b | 32 |
| 14 | 20 | cyclopropyl | -CO2Li | 0 | 33c | 32 |
| 15 | None | 64 | ||||
Pilicide:PapD, 25:95 μM. 6% RSD as determined from triplicates with compound 2.
Only the R1-cyclopropyl derivatives were evaluated for PapD binding affinity.
The reduced intensity was dependent on observed proton; 62 or 78% for 10 and 33 or 52% for 20. The tabulated value originates from protons with identical positioning on the naphthyl unit.
Representative HA-titers (the highest dilutions that still provides hemagglutination) for duplicate runs.
Not evaluated.
Precipitated.
Possible growth defect.
Previous studies have shown that there are no significant difference in biological effect between the carboxylic acid and the corresponding lithium carboxylate.31
