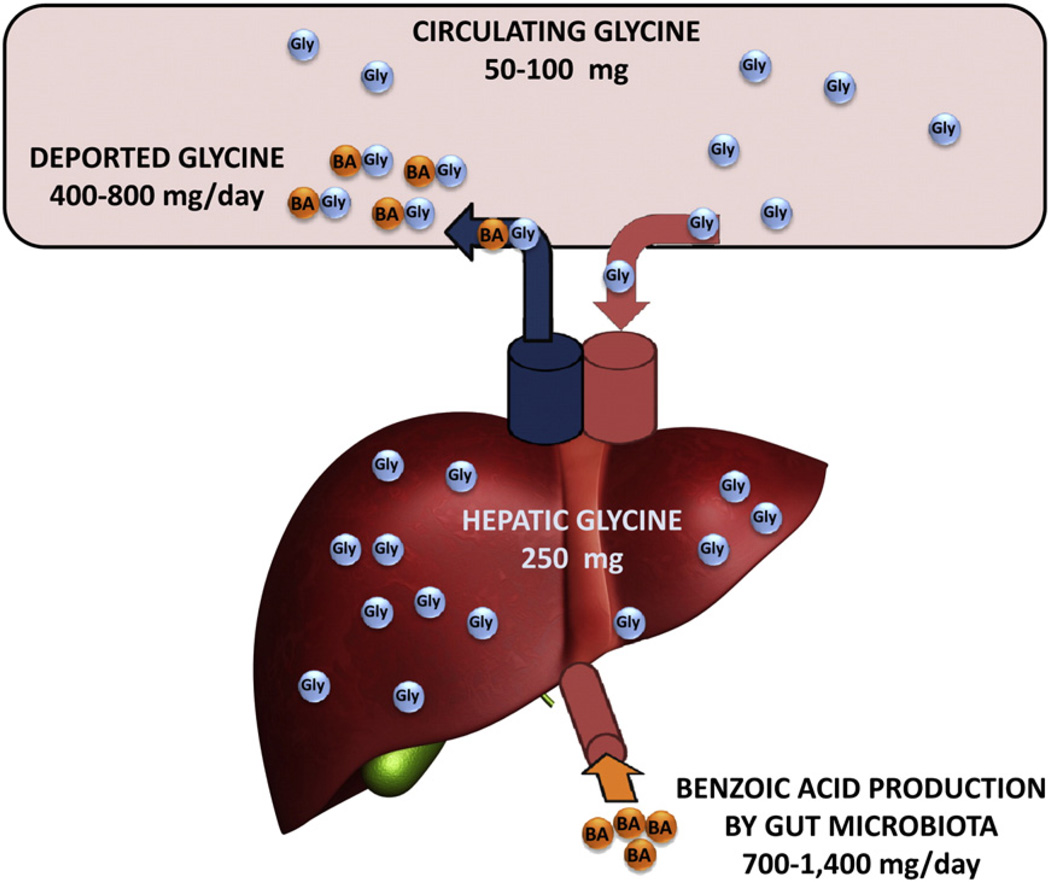
Fig. 3.
Quantitative aspects of the fate of glycine. This schematic shows that there is 50–100 mg of circulating GLY that enters the liver from the aorta into the hepatic artery, 250 mg of GLY in the liver and 400–800 mg GLY deported through the hepatic vein into the vena cava after reaction of GLY with BA in the liver. BA is produced by the gut microbiota at 700–1400 mg/day and enters the liver through the hepatic portal vein.