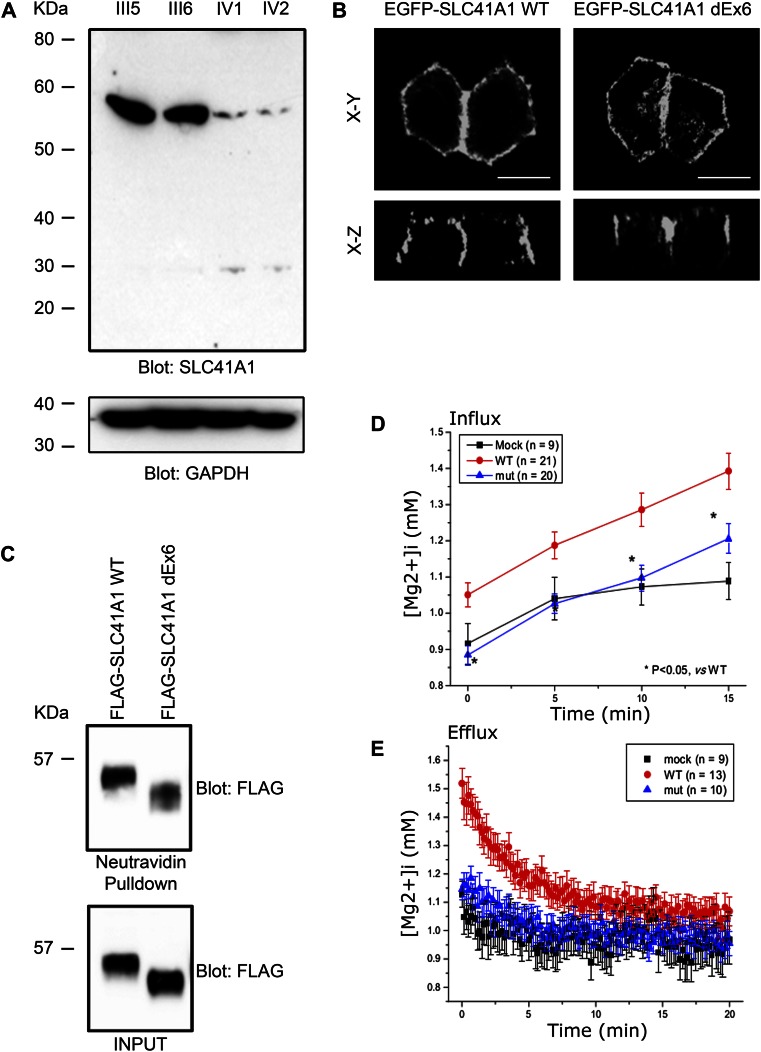
Figure 3.
The c.698G>T mutation results in reduced expression and loss of function of SLC41A1. (A) Western blot of lysates prepared from parents (III5 and III6) and affected siblings (IV1 and IV2) showing decreased expression of SLC41A1 in affected siblings. Anti–glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) Western blot was used as loading control. (B) EGFP-tagged WT SLC41A1 and SLC41A1 lacking exon 6 (dEx6) were transiently transfected into MDCKII cells. Cells were fixed and EGFP fluorescence captured by confocal microscopy. (C) HEK293 cells transiently transfected with WT or dEx6 FLAG-tagged SLC41A1 were biotinylated at the cell surface before lysis. Cell lysates were then subjected to pulldown with neutravidin beads before SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with the indicated antibodies. (D) HEK293 cells were transfected with empty vector (MOCK) WT or dEx6 EGFP-SLC41A1 before loading with mag-fura2-AM. To measure magnesium influx, cells were exposed to high Mg2+, low Na+ solution, and radiometric fluorescent images were collected to determine intracellular [Mg2+]. (E) To measure magnesium efflux, cells were treated as above and then switched into magnesium-free media, and radiometric fluorescent images were collected to determine intracellular [Mg2+]. Error bars show standard deviation.