Table 2.
Examples of serine hydrolase targets and lead inhibitors with potential therapeutic value.
| Target | Compound (Company, if applicable) | Structure | Ref(s) | Potential Indication | Developmen t Stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FAAH | OL-135 |
|
184 | inflammatory pain; nervous system disorders | preclinical |
| URB597 (Kadmus Pharmaceuticals) |
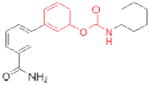
|
77 | preclinical | ||
| PF-04457845 (Pfizer) |
|
13 | Phase II | ||
| FAP/ dipeptidyl peptidases | PT-100 (Point Therapeutics) |
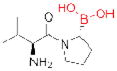
|
143, 144 | cancer | Phase III (on hold) |
| LIPG | ‘Sulfonylfuran urea 1’ (GlaxoSmithKline) |
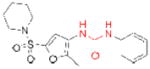
|
121 | cardiovascular disease | preclinical |
| PLA2G7 | Darapladib (GlaxoSmithKline) |
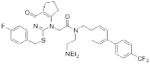
|
104 | atherosclerosis | Phase III |
| PRCP | ‘Compound 8o’ (Merck) |
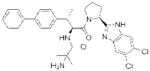
|
109 | obesity | preclinical |
| PREP | S 17092 |
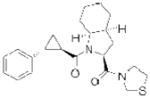
|
127 | cognitive deficits | preclinical |
| JTP-4819 (Japan Tobacco) |
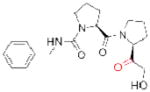
|
126 | preclinical | ||
| TGH | GR148672X (GlaxoSmithKline) |
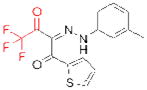
|
115 | hypertriglycerid- emia | preclinical |
The electrophilic moieties of each compound, if applicable, are colored red.
