Fig. 2. Elevated cAMP increases phosphorylated GRK7 in HEK-293 cells.
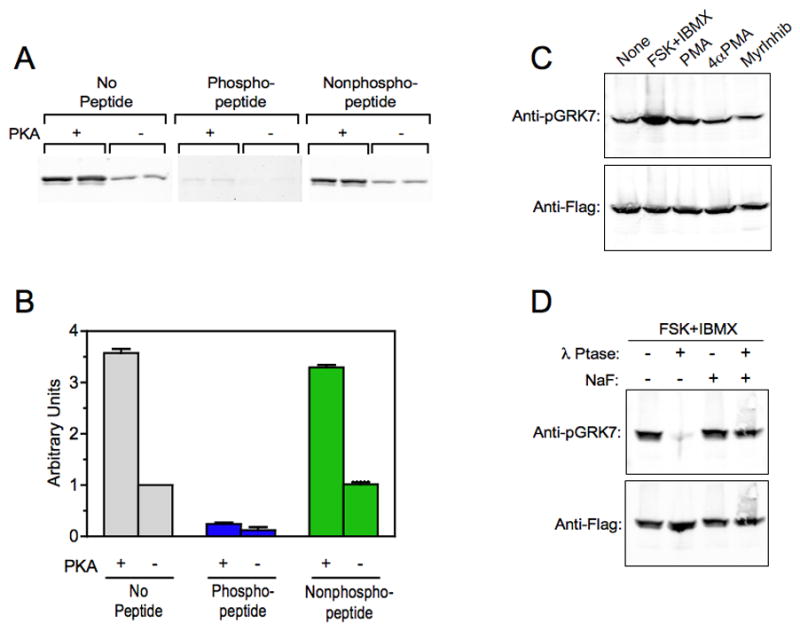
(A) Immunoblot analysis comparing the binding of the anti-pGRK7 antibody to purified, Flag-tagged human GRK7 phosphorylated by PKA (+) and untreated (−). The blots were incubated with a 1:2,000 dilution of the anti-pGRK7 antibody preincubated overnight with no peptide, phosphopeptide or nonphosphopeptide at a 10-fold excess by weight, as described in the Materials and Methods. The experiment contains duplicate samples and is representative of 2 independent experiments.
(B) Two independent experiments, including the one shown in (A), were analyzed using the Odyssey imaging system and demonstrates that the binding of anti-pGRK7 is specific for phosphorylated GRK7. Error bars represent the range between the two independent experiments.
(C) HEK-293 cells expressing GRK7 were treated with 50 μM forskolin (FSK) and 1 mM IBMX, 100 nM phorbol myristyric acid (PMA), 100 nM 4-α-myristyric acid (4αPMA), or 50 μM myristoylated PKC peptide inhibitor (MyrInhib), for 30 min at room temperature. Cell extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting using the anti-pGRK7 and anti-Flag antibodies at 1:2,000 and 1:10,000, respectively.
(D) HEK-293 cells were treated with 50 μM FSK and 1 mM IBMX for 30 min. Cell extracts were prepared with (+) or without (−) 50 mM NaF, a phosphatase inhibitor, then incubated with or without 600 units λ phosphatase (λ Ptase) for 30 min as described in the Materials and Methods, and subjected to immunoblot analysis using the same antibody dilutions as described in (C).
