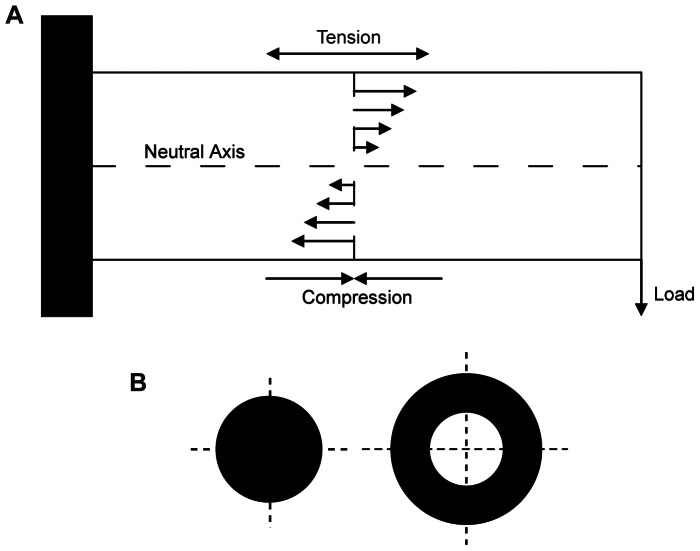
Figure 4. Simple illustrations of beam theory.
. (A) When a load is applied to a beam with one fixed end (a cantilever beam), the effect of the beam is a deflection in the direction of the force. This results in the most extreme tension on one side of the beam, and the most extreme tension on the opposite side. In the middle, there is a point where there is no tension or compression, called the neutral axis. B) Two circular cross sections of equal cortical area (black). Beam theory states the solid tube (hollow circle) will have higher resistance to bending and torsion than the solid circle due to the material being distributed further from any neutral axis.