Figure 1. Schematic representation of the structural diversity of the PP2A holoenzyme complex.
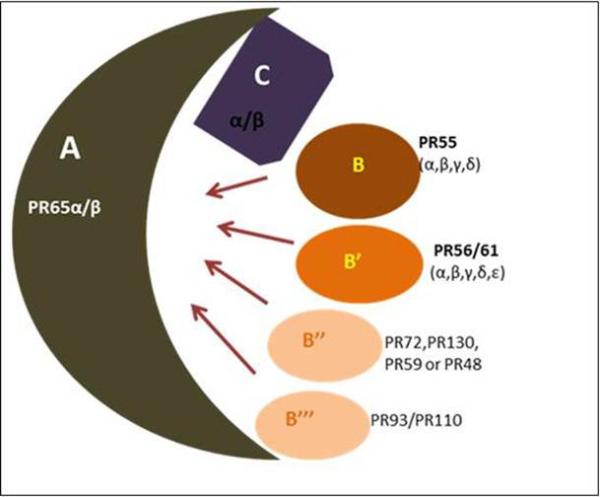
PP2A enzymes are heterotrimers consisting of core dimer sscaffold (A) and a ccatalytic (C) subunit that is associated with one of the rregulatory (B) subunits. The scaffold A and catalytic C are encoded by two distinct genes α and β. The α and β isoforms of the catalytic subunit share 97% homology. However, in the typical cell, the catalytic α isoform predominates which is 10 times more abundant than the β isoform. Similar to catalytic subunit α and β isoforms of the scaffold subunit also share 86% identity in their primary sequence. The B-type subunits were further categorized into four unrelated families: B (PR55), B’ (PR56/61), B” (PR72/130) and B’” (PR93/110). Within each B-type family, distinct genes encode various structurally related isoforms such as α, β, γ and δ.
