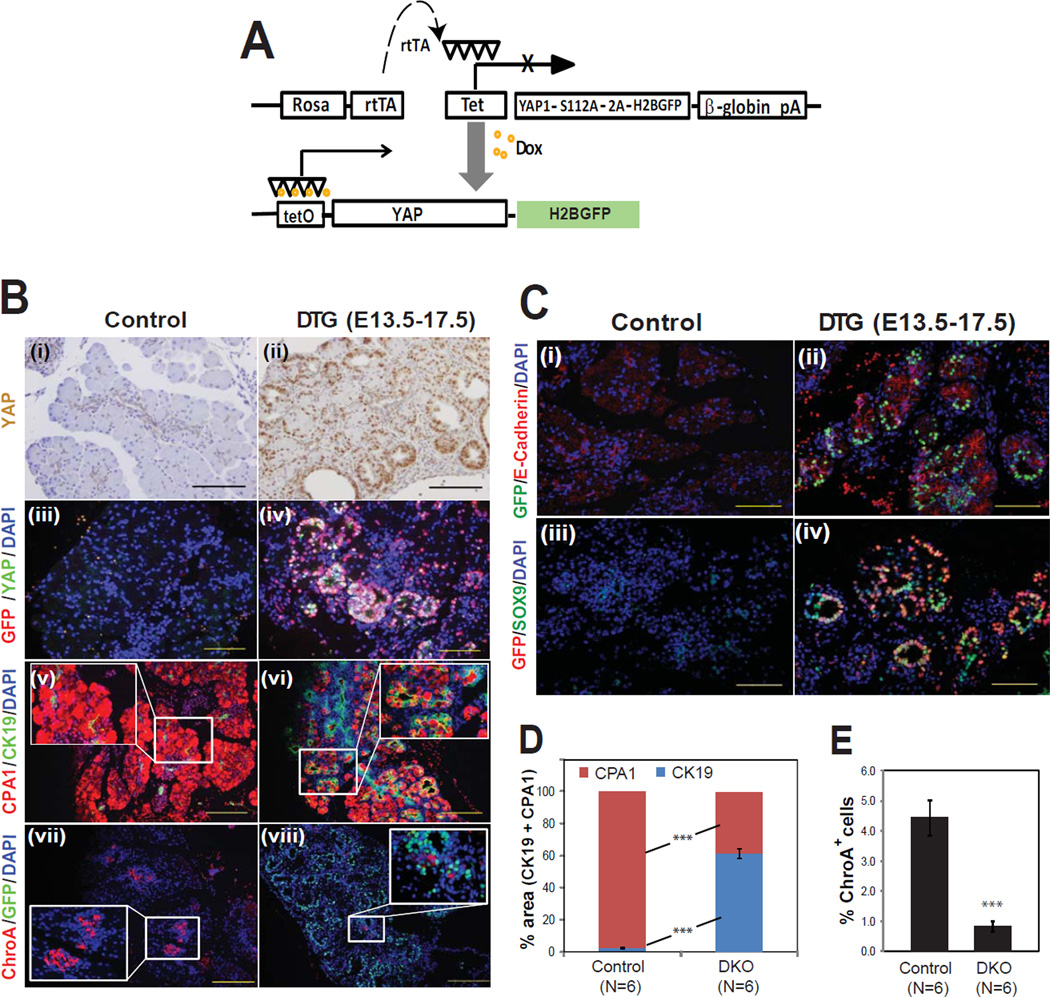
Figure 5. Reversible activation of YAP in pancreas causes acinar metaplasia and inhibits endocrine differentiation.
(A) A tetO-YAP-2A-GFP construct was inserted into the Rosa26 locus by homologous recombination and tetO-YAP-GFP mice were crossed to Rosa-rtTA mice. In bigenic (DTG) mice, transgene expression is dependent upon doxycycline.
(B) The YAP-GFP transgene was induced with doxycycline from E13.5 – E17.5 and pancreata were examined at E17.5 by H&E and immunofluorescence for acinar (CPA1), ductal (CK19), and endocrine (ChroA) markers.
(C) Co-immunofluorescence for GFP and E-cadherin or Sox9 revealed that transgene expression was most abundant in the epithelium.
(D, E) Quantification of changes in relative percentage of acinar/ductal area (D; measured by CPA1 and CK19 staining) and endocrine area (E; measured by ChroA staining) in control versus DTG pancreata (mean +/− SD; ***, P<0.001). Scale bar: 100 µM.