Figure 6. L-Fabp deletion attenuates hepatic fibrosis in TFF-fed mice.
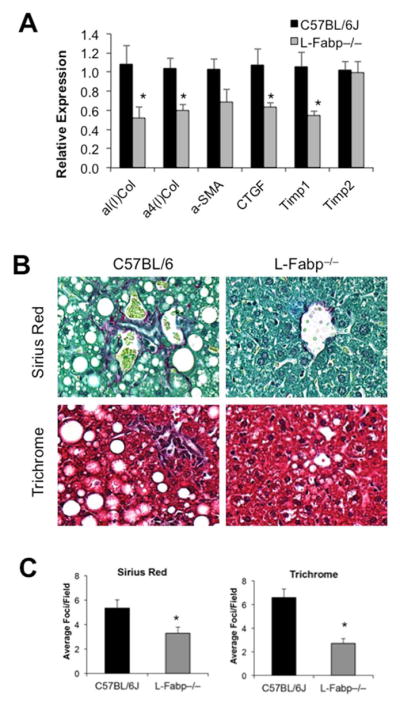
Liver tissue from C57BL/6J and L-Fabp−/− mice fed a TFF diet for 16 weeks was processed for histology or RNA isolation. (A). Real-time PCR analysis of pro-fibrogenic genes, including Type 1 and Type IV alpha collagens (α1(I) Col and α4(I) Col), alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 and 2 (TIMP1 and TIMP2) in liver tissue from each genotype; n=7–8 per group. Asterisks indicate p<0.05 vs C57BL/6J controls. (B). Picro-Sirius Red and Trichrome staining of collagens in liver tissue from each group of mice. A representative image from each genotype is presented. (C). Blind calculation of fibrotic foci per field in Picro-sirius red (left panel) and Trichrome (right panel) stained slides. Data represent average number of fibrotic regions per field, with 10 fields counted per slide; mean ± SE. n=7 C57BL/6J, 8 L-Fabp−/− mice. Asterisks indicate p<0.05 vs C57BL/6J controls.
