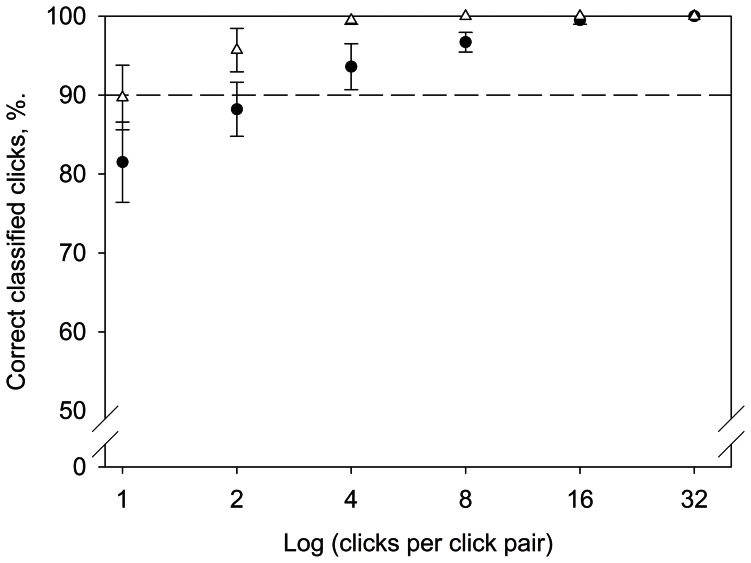
Figure 3. Acoustic species discrimination.
Dall’s (circles) and BC-harbour porpoises (triangles) can be separated by means of differences in centroid frequency using a criterion of 139 kHz in a Monte Carlo simulation. The clicks were first filtered with the harbour porpoise’ audiogram (see text) to simulate porpoise reception. The dashed line indicates 90% correctly classified clicks. Such differences may also be useful in passive acoustic monitoring, provided there is fine-scale frequency resolution in the PAM dataloggers. The percentage correct (y-axis) for each click pair is the mean of ten rounds of randomly drawing 100 click pairs consisting of N clicks per pair (x-axis), and the values are shown with the standard error of the mean. The clicks included are one on-axis click for each five off-axis clicks.