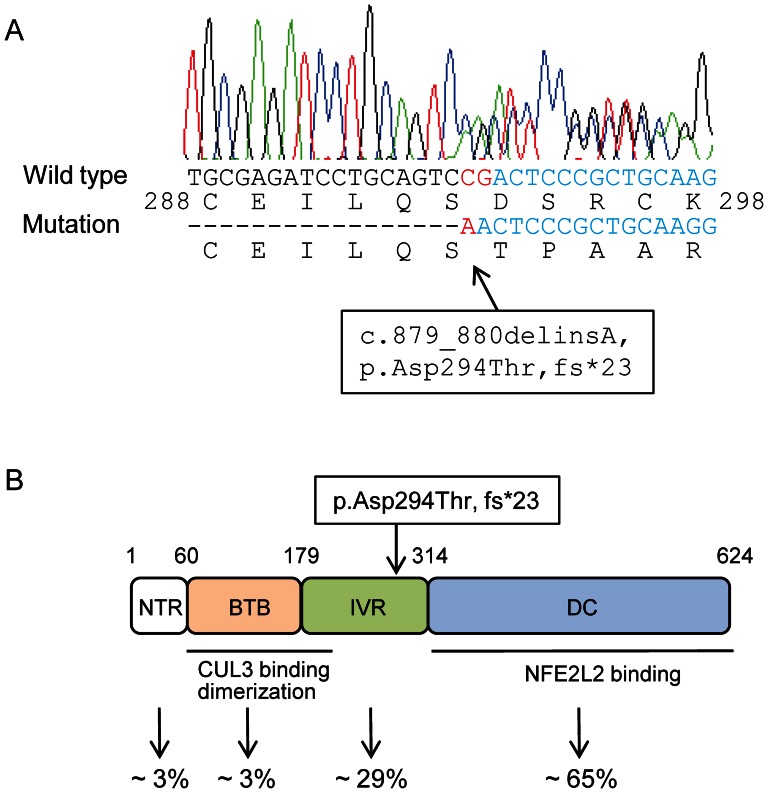
Figure 3. Identification of a heterozygous mutation in KEAP1 .
(A) The result of Sanger sequencing of proband DNA showed the c.879_880delinsA mutation (red), resulting in a 1-base deletion and a frameshift (p.Asp294Thr, fs*23) in KEAP1. (B) Domain structure and mutation location in the KEAP1 protein. The protein consists of an N-terminal region (NTR; amino acids 1 to 60), a BTB domain (amino acids 61 to 179), an intervening region (IVR; amino acids 180 to 314) and a DC domain (amino acids 315 to 624). The BTB and N-terminal portion of IVR is responsible for dimerisation and the interaction with CUL3. The DC domain is also critical for the interaction with NFE2L2. The p.Asp294Thr, fs*23 mutation is located in the IVR. The reported frequencies of the somatic mutations observed in each domain in cancer cells are shown at the bottom [32].