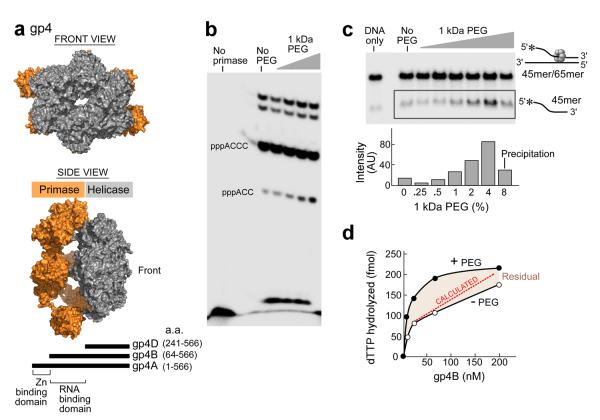
Figure 3. The effect of macromolecular crowding on gp4 activity.
(a) Front (top panel) and side View (middle panel)of a gp4 model. Gp4 has both primase and helicase activities in the same polypeptide chain. Subunits of the heptameric crystal structure of gp4B (PDB entry 1q5749) were aligned with the hexameric helicase fragment (PDB ID code: 1e0k30) and primase fragment (PDB entry 1nui44) of gp4. Schematic representation of gp4 constructs (bottom). The boundaries for the helicase and primase domains of gp4 are depicted45. The three constructs containing the C-terminal helicase domain of gp4 are denoted as gp4A, B, and D. Residue numbers are as indicated. The figure was created using PyMOL (http://www.pymol.org). (b) Effect of PEG on oligonucleotide synthesis by primase fragment. The standard reaction contained the oligonucleotide 5'-GGGTCA10-3' containing the primase recognition sequence, 200 μM [α-32P]-CTP and ATP, and increasing amounts of 1kDa PEG (0, 1.25, 2.5, 5, 10%) in a buffer containing 40 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 10 mM MnCl2, 10 mM DTT, and 50 mM potassium glutamate. The quenched samples were loaded onto 25% polyacrylamide sequencing gel containing 3 M urea and visualized using autoradiography. (c) Effect of PEG on the DNA unwinding activity of gp4B. The DNA fork depicted (right) was prepared by partially annealing a 5'–32P labeled 45-mer oligonucleotide to a 65-mer oligonucleotide. DNA unwinding activity was performed in a standard reaction containing 40 mM Tris–HCl (pH 7.5), 50 mM potassium glutamate, increasing amounts of PEG 1 kDa (0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4 and 8%), and 400 nM of gp4B. The gel shows the separation of unwound ssDNA (bottom) from the dsDNA substrate in a 10% non-denaturing gel. (d) Effect of highly crowding conditions (8% PEG) on the DNA-dependent dTTPase activity of gp4B. The dTTPase activity was measured in the presence of 5 mM dTTP and 8% PEG and with various concentrations of gp4B (0–200 nM). Difference in the dTTPase activity in the presence and absence of high concentration of PEG is denoted as residual.