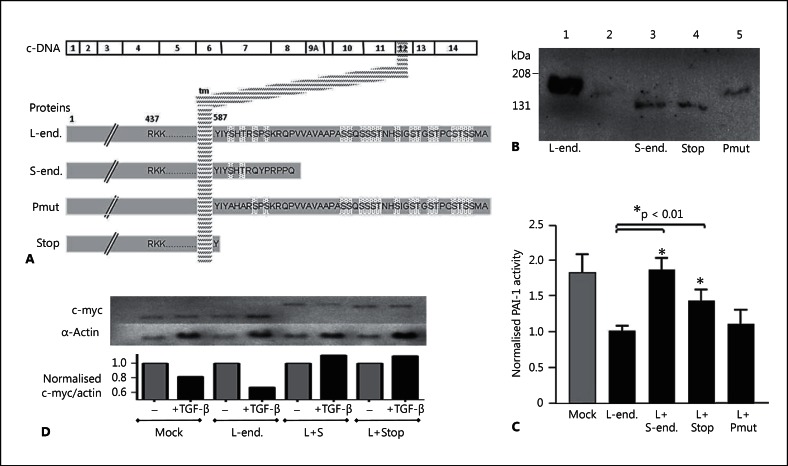
Fig. 4.
Natural and recombinant endoglin variants. A Illustration of the variants with respect to the transmembrane domain and cytoplasmic tail (end. = endoglin). L-endoglin and S-endoglin are naturally occurring endoglin species; the artificial mutants have the 2 cytoplasmic serine residues conserved between L- and S-endoglin mutated to alanines (Pmut), or a stop codon in place of the second cytoplasmic amino acid of endoglin (I588X; Stop). B Western blot data of total cell protein extracted from L6E9 cells stably transfected with L-endoglin (lane 1), or the mock-transfected L6E9 cells transiently transfected with expression vectors for S-endoglin (lane 3), the truncated L-endoglin I588X stop mutant (lane 4) or the phosphorylation mutant (lane 5). C Modulation of PAI-1 promoter activity by stable expression of L-endoglin in L6E9 rat myoblasts (lanes 2-5) and subsequent modulation by transient transfection of empty vector (lanes 1 and 2) or other endoglin species (lanes 3-5): Basal PAI-1 activity was significantly (p < 0.0001) downregulated by stable transfection of L-endoglin. Transient transfection of S-endoglin, the truncation mutant, but not the phosphorylation mutant resulted in PAI-1 activities not different to the mock stable transfectants, L6E9 rat myoblasts not expressing L-endoglin. D Modulation of c-myc and α-actin expression in mock-transfected L6E9 or L6E9 stably expressing L-endoglin following transient transfection with an empty vector (mock; L-endoglin); S-endoglin or the truncated endoglin construct, before 24 h treatment with normal media or media supplemented with 3 μg/ml TGF-β1.