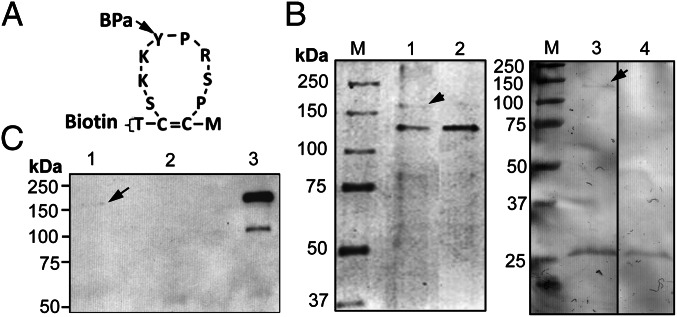
Fig. 1.
Identification of APN as the GBP3.1 receptor. (A) A double derivatized synthetic GBP3.1, with a biotin residue at the N terminus and a UV-cross-linking residue (pbenzoyl-l- phenylalanine, BPa) replacing the tyrosine residue in the loop was used for receptor identification. (B) Coomassie Blue-stained SDS-polyacrylamide gel of proteins interacting with synthetic GBP3.1 in a pull-down experiment. The GBP3.1–receptor protein complex was pulled down by streptavidin agarose beads. Lane 1, GBP3.1 incubated with pea aphid gut and UV-cross-linked to interacting proteins. The ∼180-kDa protein (arrow) was consistently pulled down following UV-cross-linking to GBP3.1. Lane 2, GBP3.1 incubated with pea aphid gut, without UV-cross-linking. Lane 3, streptavidin beads with pea aphid gut only, showing the ∼140-kDa gut protein (arrow) pulled down by the streptavidin beads. Lane 4, streptavidin beads only. Molecular mass standards (M) are indicated. (C) Western blot analysis with anti-pea aphid APN antiserum confirmed the identity of the GBP3.1-interacting protein from pull-down experiments as APN. Lane 1, pea aphid gut proteins UV-cross-linked to GBP3.1. Lane 2, pea aphid gut proteins incubated with GBP3.1 without UV-cross-linking before pull-down. Lane 3, pea aphid gut proteins (positive control).