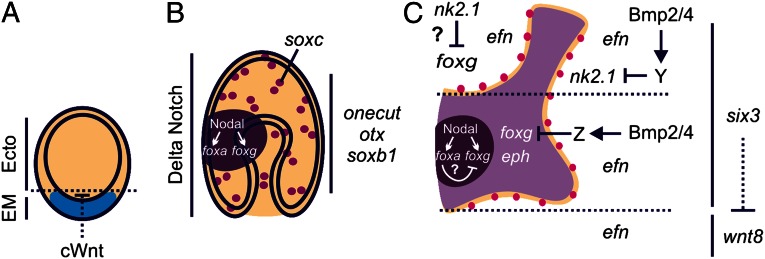
Fig. 5.
Model for localized patterning of neurons within a broad neurogenic potential ectoderm. (A) Canonical Wnt (cWnt) signaling initially establishes endomesoderm (EM, blue) from ectoderm (Ecto, tan). A suite of neurogenic genes including onecut-, otxßb-, and soxb1 are expressed throughout the ectoderm of (A) blastulae and (B) gastrulae. (B) Delta Notch signaling patterns distinct soxc-expressing cells within the broad neurogenic potential ectoderm. Nodal signaling establishes foxg and foxa expression within the ventral ectoderm (dark purple). (C) During late gastrulation, foxg expression clears from the stomodeal (mouth) ectoderm and a foxg-CBD (light purple) is shaped by Bmp2/4 signaling and Six3. The creation of this foxg-CBD, distinguishes between eph- and efn-expressing ectodermal territories. Differentiated neurons (magenta) form along this boundary. Dotted lines in C denote the position of the foxg-CBD within the ectoderm along the AP axis; six3-expressing anterior ectoderm extends upward from the bottom dotted line and includes the anterior pole ectoderm, above the top dotted line.