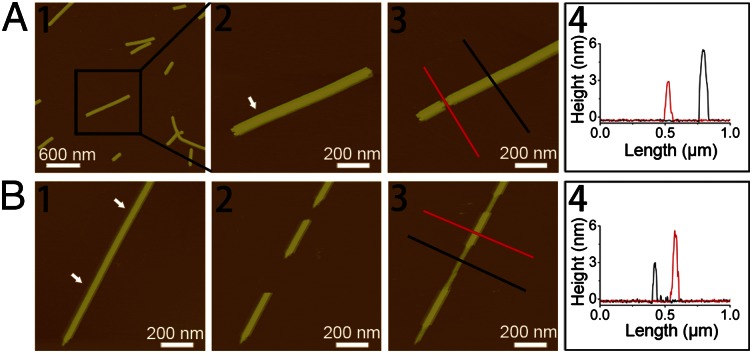
Fig. 3.
(A) AFM height images and section analysis indicating a height of ∼3 nm of the sublayer after removing the top layer by AFM mechanical manipulation. (A1 and A2) Original double-layered GAV-9 nanofilaments. (A3) Top layer was removed by AFM manipulation. (A4) Section analysis of the sublayer and the double-layered nanofilaments as indicated by lines in A3. (B) Tapping-mode AFM height images indicating the extension of GAV-9 nanofilaments with a height of ∼3 nm after removing two parts of preformed nanofilaments with a height of ∼6 nm. (B1) Original double-layered GAV-9 nanofilaments. (B2) Two gaps appeared on the original nanofilament after AFM mechanical manipulation. (B3) GAV-9 molecules filled the gaps, resulting in formation of a sublayer with a height of ∼3 nm. (B4) Section analysis of the sublayer and the double-layered nanofilaments is shown as indicated with lines in B3. The arrows in A2 and B1 indicate the positions on the preformed peptide nanofilaments mechanically manipulated by the tip of atomic force microscope. Both of the experiments were carried out on mica under aqueous solution containing 50 mM MgCl2.