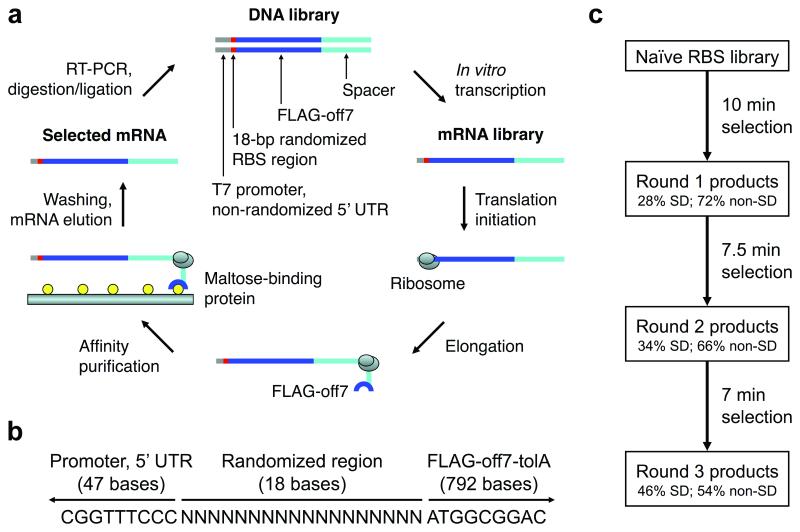
Figure 1.
Ribosome display method, library context, and selection scheme. a) In our adaptation of ribosome display for the selection of efficiently translated sequences, the naïve DNA library contained an 18-bp randomized RBS region before the start codon. Selection pressure was increased over multiple rounds by progressively limiting the time of in vitro translation. b) The DNA context of the randomized RBS region is shown. The T7 promoter and 5′ UTR stem-loop derived from the ribosome display vector, pRDV, are upstream (47 bases in the DNA construct, 21 bases in the mRNA transcript). The coding region (downstream) contains a fusion protein with a FLAG tag, Off7 (a designed ankyrin repeat protein which binds maltose-binding protein), TolA (an unstructured spacer derived from E. coli tolA which allows Off7 to exit the ribosomal tunnel and fold properly), and no stop codon. c) The selection scheme is shown. The naïve RBS library was subjected to three selection rounds of increasing stringency: 10 min, 7.5 min, and 7 min translation. SD sequences were enriched between rounds, but many non-SD sequences remained in the pool after three rounds. Adapted from (8). 5′ UTR, 5′ untranslated region; RBS, ribosome binding site; SD, Shine-Dalgarno.