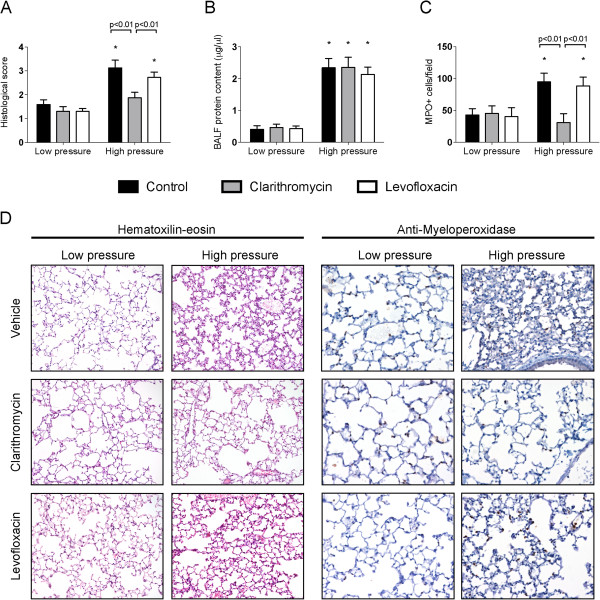
Figure 1.
Lung injury after mechanical ventilation. Structural lung injury increased with high-pressure ventilation in vehicle- and levofloxacin-treated animals, but not in mice receiving clarithromycin (A). Alveolocapillary permeability, assessed by measurement of protein content in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), increased after high-pressure ventilation irrespective of the treatment (B). Neutrophil recruitment increased after high-pressure ventilation in vehicle- and levofloxacin-treated animals. However, clarithromycin-treated animals showed no differences in neutrophil counts compared to mice ventilated with low pressures (C). Representative sections are shown in panel D. *p < 0.05 in post-hoc tests compared to low-pressure ventilated counterparts.