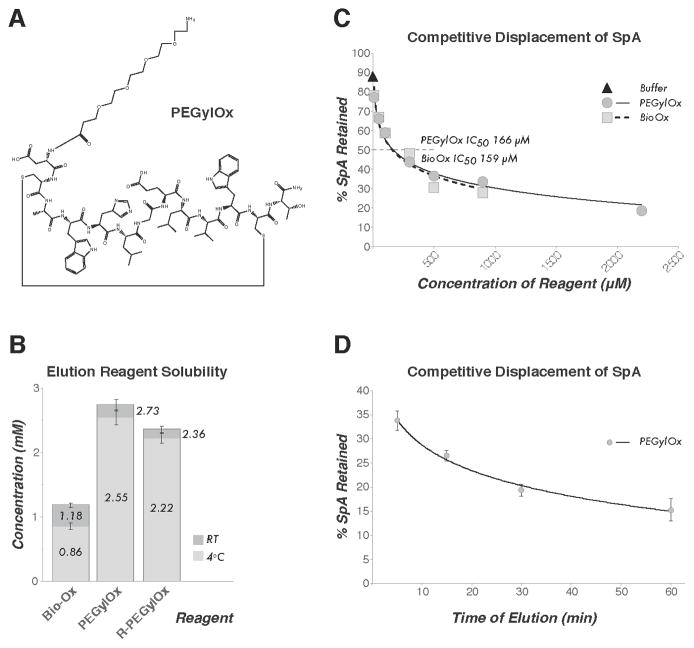
Figure 1. PEGylation of FcIII peptide increases solubility and maintains competitive displacement of S. aureus Protein A (SpA) from mammalian IgG.
(A) The chemical structure of PEGylOx. (B) The concentrations of Bio-Ox, PEGylOx, and R-PEGylOx at room temperature (RT) or 4°C, as determined by UV280 spectrophotometry on three independent aliquots of lyophilized peptide suspended in the described buffered solution. Error bars indicate the standard deviation (SD) (C) The percentage of SpA retained by immobilized rabbit IgG after treatment with differing concentrations of Bio-Ox or PEGylOx for 1 h at RT – as determined by image densitometry of Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE gels (detailed in Supplementary Section S3). for both reagents is indicated. All values are A buffer only control is included, and the IC50 the average of duplicate experiments. (D) The percentage of SpA retained by immobilized rabbit IgG after treatment with a saturated solution of PEGylOx for 5, 15, 30, or 60 min. All values are the average of triplicate experiments with SD indicated.