Figure 5.
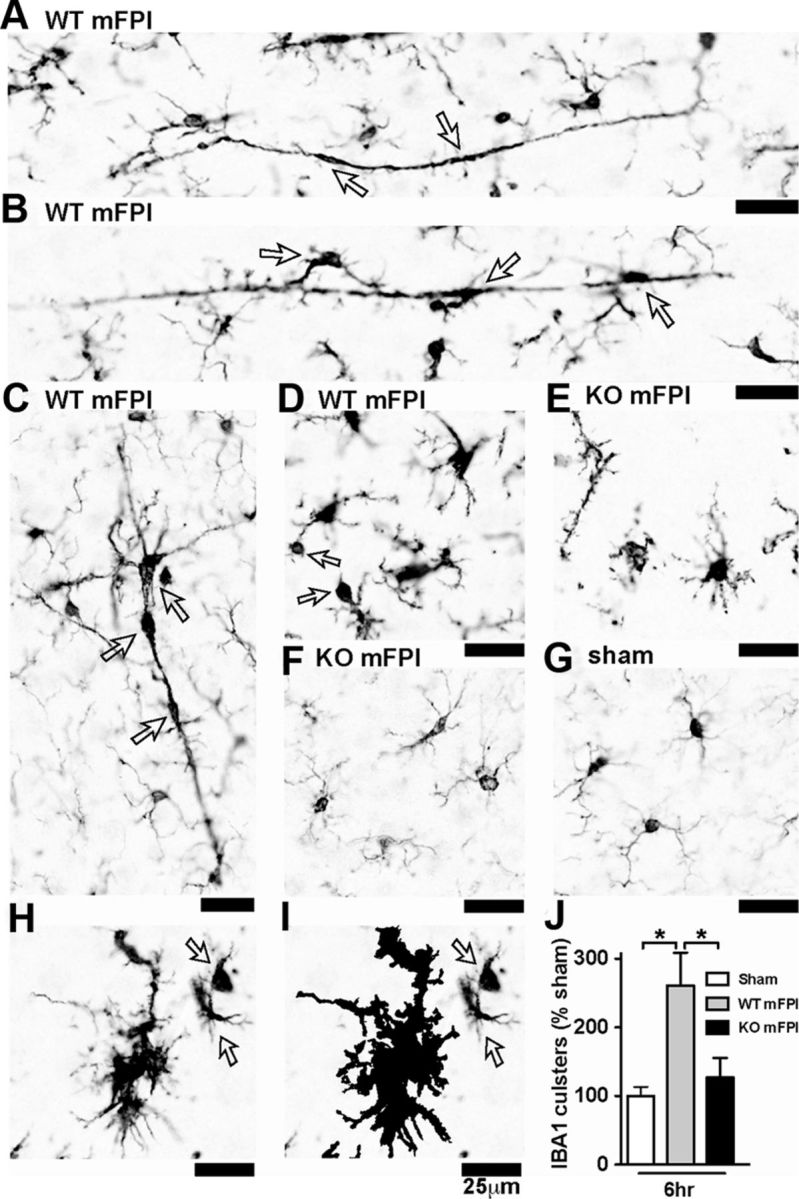
Microglia clustering is dependent on p38α KO after a diffuse TBI. A–D, IBA1 IHC shows the spectrum of microglia activation seen in the WT mice 6 h after the diffuse brain injury. Note the long, rod-shaped microglia (A), trains of multiple microglia in plane with the axonal columns in the cortex (B), and multiple microglia in the shape of a layer-V pyramidal cell (C), as well as IBA1+ cells with retracted processes with large swellings (D). In contrast, the p38α KO mice exhibited thin ramified microglia processes (E) or looked morphologically similar (F) to sham-injured mice (G). A cluster of microglia from a WT mFPI mouse shows the IBA1 staining (H), and the Aperio nuclear algorithm generated markup shows the reliable detection of the microglia clusters (demonstrated here as the black markup) and not individual cells (arrows) (I). Quantification shows a significant increase in IBA1 clusters in the WT-injured mice at 6 h after injury (J). Data are presented as percentage of sham; n = 6–8 per group. *p < 0.05.
