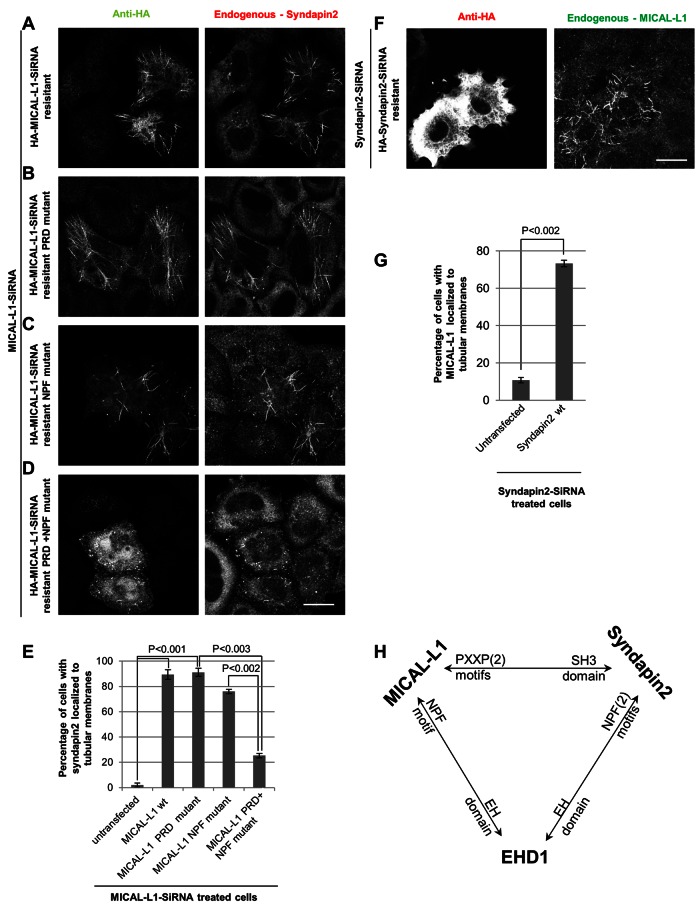
FIGURE 3:
Complex interactions between MICAL-L1, Synd2, and EHD1 in tubular localization and biogenesis. (A–D) Cells treated for 72 h with MICAL-L1 siRNA were transfected for the last 48 h with either siRNA-resistant, wild-type, HA-tagged MICAL-L1 or mutant constructs. The cells were then immunostained with anti-HA and anti-Synd2 antibodies. Bar, 10 μm. (E) HeLa cells treated as in A were quantified to assess the percentage of cells with Synd2 localized to tubular membranes. Error bars, SE. (F) Cells treated for 72 h with Synd2 siRNA were transfected for the last 48 h with siRNA-resistant, wild-type, HA-tagged Synd2. Cells were then immunostained with anti-HA and anti–MICAL-L1 antibodies. Bar, 10 μm. (G) HeLa cells treated as in F were quantified to assess the percentage of cells with MICAL-L1 localized to tubular membranes. Error bars, SE. (H) Model illustrating the interaction profile between MICAL-L1, Synd2, and EHD1.